Therapy of early breast cancer: current status and perspectives
- PMID: 40261372
- PMCID: PMC12334469
- DOI: 10.1007/s00404-025-08028-0
Therapy of early breast cancer: current status and perspectives
Abstract
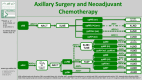
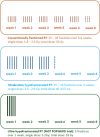
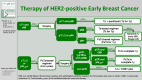
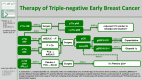
Medical advancements in breast cancer are truly remarkable. Especially in recent years, numerous new therapeutics have been approved and surgical strategies have been de-escalated for specific patient groups. In the therapeutic setting, CDK4/6 inhibitors as oral maintenance therapy in early breast cancer and immune checkpoint inhibitors (Pembrolizumab) for triple-negative breast cancer (BC) are noteworthy. In the surgical field, prospective randomized controlled trials have currently explored the possibility to deescalate axillary surgery by omitting sentinel lymph node excision (INSEMA, SOUND). As a result, there have been significant improvements in prognosis and a reduction in surgical morbidity for patients. Many exciting trials are underway, and it remains to be seen whether antibody-drug conjugates beyond trastuzumab emtansine, will find their way into the treatment lines for early-stage BC. Furthermore, the integration of artificial intelligence in both diagnostics and treatment recommendation evaluation is a promising area with great potential.
Keywords: Early breast cancer; Future perspectives; HER2-positive; Hormone-receptor positive; Surgical de-escalation; Triple-negative.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Conflict of interest: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


References
-
- Zentrum für Krebsregisterdaten, R.K.I. Brustkrebs (Mammakarzinom). Available online: https://www.krebsdaten.de/Krebs/DE/Content/Krebsarten/Brustkrebs/brustkr.... Accessed on 02 Jan 2025.
-
- Schoffer O, Wimberger P, Gerken M, Bierbaum V, Bobeth C, Rößler M, Dröge P, Ruhnke T, Günster C, Kleihues-van Tol K et al (2024) Treatment in certified breast cancer centers improves chances of survival of patients with breast cancer. Evid Based Health Care Data WiZen Study 84:153–163. 10.1055/a-1869-1772 - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

