Ketogenic diet improves disease activity and cardiovascular risk in psoriatic arthritis: A proof of concept study
- PMID: 40261944
- PMCID: PMC12013891
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0321140
Ketogenic diet improves disease activity and cardiovascular risk in psoriatic arthritis: A proof of concept study
Abstract
Objectives: Very low-calorie ketogenic diet (VLCKD) is a low-carbohydrate, low-calorie regimen that leads to rapid weight loss and may reduce inflammation. This study assessed the impact of VLCKD on anthropometric measurements, inflammatory biomarkers, metabolic health, and cardiovascular risk in psoriatic arthritis (PsA) patients moderately overweight or in class I obesity.
Methods: A proof-of-concept single-arm monocentric study involved PsA patients undergoing a 9-week VLCKD treatment. Patients with Body Mass Index (BMI) ≥27 and <35, in stable (≥6 months) remission or low disease activity, as defined by Disease Activity in PSoriatic Arthritis (DAPSA) score, were included and underwent nutritional evaluations every 3 weeks. The study analyzed changes after the VLCKD intervention and the association between changes of anthropometric parameters and clinical and laboratory variables.
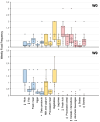
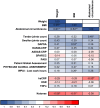
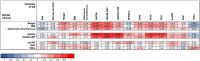
Results: Twenty patients were enrolled since April 2022 and completed the study in May 2023. Median baseline BMI was 30.9 (interquartile range 29.1-33) kg/m². All participants exhibited low baseline disease activity, which correlated with BMI (Spearman's correlation coefficient (rs)=0.59,p=0.007). Following VLCKD, significant improvements were observed in all anthropometric measures (BMI -3.5[-4;-2.6]), PsA activity (DAPSA -6.1[-16.8;3.7]), cardiovascular parameters (SCORE2 index -0.2[-0.7;0.1]), insulin resistance (Homeostatic Model Assessment-Insuline Resistance -2.1[-1.1;-3.0]), and lipid profile. Most inflammatory biomarkers remained within normal limits. BMI reduction correlated with changes in DAPSA scores (rs=0.52,p=0.020). Patients with higher baseline weight or clinical activity experienced more pronounced improvements.
Conclusions: VLCKD significantly improved PsA activity and metabolic health. Patients with a higher BMI and less controlled disease are particularly motivated and could benefit more from VLCKD compared to those with lower BMI or better disease control.
Copyright: © 2025 Ramonda et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
References
-
- Kris-Etherton PM, Harris WS, Appel LJ. Omega-3 fatty acids and cardiovascular disease: New recommendations from the American Heart Association. Circulation. 2021;143(6). - PubMed
-
- Di Giuseppe D, Wallin A, Bottai M, Askling J, Wolk A. Long-term intake of dietary long-chain n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids and risk of rheumatoid arthritis: a prospective cohort study of women. Ann Rheum Dis. 2014;73(11):1949–53. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

