RFX3 is essential for the generation of functional human pancreatic islets from stem cells
- PMID: 40263183
- PMCID: PMC12176927
- DOI: 10.1007/s00125-025-06424-4
RFX3 is essential for the generation of functional human pancreatic islets from stem cells
Abstract
Aims/hypothesis: The role of regulatory factor X 3 (RFX3) in human pancreatic islet development has not been explored. This study aims to investigate the function of RFX3 in human pancreatic islet development using human islet organoids derived from induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs), hypothesising that RFX3 regulates human islet cell differentiation.
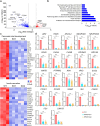
Methods: We generated RFX3 knockout (RFX3 KO) iPSC lines using CRISPR/Cas9 and differentiated them into pancreatic islet organoids. Various techniques were employed to assess gene expression, cell markers, apoptosis, proliferation and glucose-stimulated insulin secretion. Single-cell RNA-seq datasets from human embryonic stem cell-derived pancreatic islet differentiation were re-analysed to investigate RFX3 expression in specific cell populations at various developmental stages. Furthermore, bulk RNA-seq was conducted to further assess transcriptomic changes. RFX3 overexpression was implemented to reverse dysregulated gene expression.
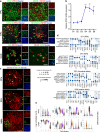
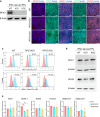
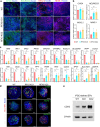
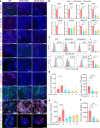
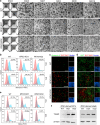
Results: RFX3 was found to be highly expressed in pancreatic endocrine cell populations within pancreatic progenitors (PPs), endocrine progenitors (EPs) and mature islet stages derived from iPSCs. Single-cell RNA-seq further confirmed RFX3 expression across different endocrine cell clusters during differentiation. The loss of RFX3 disrupted pancreatic endocrine gene regulation, reduced the number of hormone-secreting islet cells and impaired beta cell function and insulin secretion. Despite a significant reduction in the expression levels of pancreatic islet hormones, the pan-endocrine marker chromogranin A remained unchanged at both EP and islet stages, likely due to an increase in the abundance of enterochromaffin cells (ECs). This was supported by our findings of high EC marker expression levels in RFX3 KO EPs and islets. In addition, RFX3 loss led to smaller islet organoids, elevated thioredoxin-interacting protein levels and increased apoptosis in EPs and islets. Furthermore, RFX3 overexpression rescued the expression of dysregulated genes in RFX3 KO at the PP and EP stages.
Conclusions/interpretation: These findings underscore the crucial role of RFX3 in regulating human islet cell differentiation and its role in suppressing EC specification. These insights into RFX3 function have implications for understanding islet biology and potential diabetes susceptibility.
Data availability: The RNA-seq datasets have been submitted to the Zenodo repository and can be accessed via the following links: DOI https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.13647651 (PPs); and DOI https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.13762055 (SC-islets).
Keywords: Differentiation; Endocrine pancreas; Enterochromaffin cells; Transcription factor; iPSC model.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Data availability: The RNA-seq datasets have been submitted to the Zenodo repository and can be accessed via the following links: DOI https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.13647651 (PPs); and DOI https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.13762055 (SC-islets). Funding: Open Access funding provided by the Qatar National Library. This work was funded by grants from Sidra Medicine (SDR400217) and QBRI (QBRI-HSCI Project 1). NA, the co-first author of this article, is a PhD student with a scholarship funded by QRDI (GSRA9-L-1-0511-22008). Authors’ relationships and activities: SH is a co-founder and shareholder of Sequantrix GmbH and has received research funding from Novo Nordisk and Askbio. The authors declare that there are no other relationships or activities that might bias, or be perceived to bias, their work. Contribution statement: BM, NA, AKE performed the experiments and analysed the data. NA and AKE conducted all revision experiments. SI and SH analysed the sequencing data. BM and EMA wrote the manuscript. EMA conceived and designed the study, supervised the project, and analysed and interpreted the data. All authors critically reviewed the article and approved the final version of the manuscript. EMA is the guarantor of this work.
Figures

References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

