UKB-MDRMF: a multi-disease risk and multimorbidity framework based on UK biobank data
- PMID: 40263246
- PMCID: PMC12015417
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-025-58724-3
UKB-MDRMF: a multi-disease risk and multimorbidity framework based on UK biobank data
Abstract
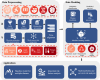
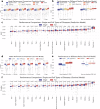
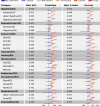
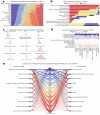
The rapid accumulation of biomedical cohort data presents opportunities to explore disease mechanisms, risk factors, and prognostic markers. However, current research often has a narrow focus, limiting the exploration of risk factors and inter-disease correlations. Additionally, fragmented processes and time constraints can hinder comprehensive analysis of the disease landscape. Our work addresses these challenges by integrating multimodal data from the UK Biobank, including basic, lifestyle, measurement, environment, genetic, and imaging data. We propose UKB-MDRMF, a comprehensive framework for predicting and assessing health risks across 1560 diseases. Unlike single disease models, UKB-MDRMF incorporates multimorbidity mechanisms, resulting in superior predictive accuracy, with all disease types showing improved performance in risk assessment. By jointly predicting and assessing multiple diseases, UKB-MDRMF uncovers shared and distinctive connections among risk factors and diseases, offering a broader perspective on health and multimorbidity mechanisms.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
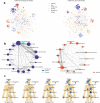
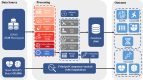
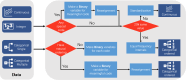
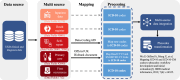
Similar articles
-
How group structure impacts the numbers at risk for coronary artery disease: polygenic risk scores and nongenetic risk factors in the UK Biobank cohort.Genetics. 2024 Jul 8;227(3):iyae086. doi: 10.1093/genetics/iyae086. Genetics. 2024. PMID: 38781512 Free PMC article.
-
A semicompeting risks model with an application to UK Biobank data to identify risk factors for diabetes onset and progression.Biometrics. 2025 Apr 2;81(2):ujaf003. doi: 10.1093/biomtc/ujaf003. Biometrics. 2025. PMID: 40417914
-
Depression and physical multimorbidity: A cohort study of physical health condition accrual in UK Biobank.PLoS Med. 2025 Feb 13;22(2):e1004532. doi: 10.1371/journal.pmed.1004532. eCollection 2025 Feb. PLoS Med. 2025. PMID: 39946376 Free PMC article.
-
[A review on the application of UK Biobank in neuroimaging].Sheng Wu Yi Xue Gong Cheng Xue Za Zhi. 2021 Jun 25;38(3):594-601. doi: 10.7507/1001-5515.202012059. Sheng Wu Yi Xue Gong Cheng Xue Za Zhi. 2021. PMID: 34180206 Free PMC article. Review. Chinese.
-
Advancing human genetics research and drug discovery through exome sequencing of the UK Biobank.Nat Genet. 2021 Jul;53(7):942-948. doi: 10.1038/s41588-021-00885-0. Epub 2021 Jun 28. Nat Genet. 2021. PMID: 34183854 Review.
References
-
- Tan, K. H. X. et al. Cohort profile: the Singapore multi-ethnic cohort (mec) study. Int. J. Epidemiol.47, 699–699j (2018). - PubMed
-
- Wan, E.Y.F. et al. Association of covid-19 with short-and long-term risk of cardiovascular disease and mortality: a prospective cohort in UK biobank. Cardiovasc. Res. 119, 1718–1727 (2023). - PubMed
-
- Cui, H. et al. scgpt: toward building a foundation model for single-cell multi-omics using generative AI. Nat. Methods21, 1470–1480 (2024) - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

