Structure of a lasso peptide bound ETB receptor provides insights into the mechanism of GPCR inverse agonism
- PMID: 40263271
- PMCID: PMC12015262
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-025-57960-x
Structure of a lasso peptide bound ETB receptor provides insights into the mechanism of GPCR inverse agonism
Abstract
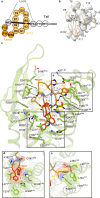
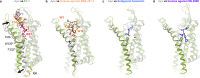
Lasso peptides exhibit a unique lariat-like knotted structure imparting exceptional stability and thus show promise as therapeutic agents that target cell-surface receptors. One such receptor is the human endothelin type B receptor (ETB), which is implicated in challenging cancers with poor immunotherapy responsiveness. The Streptomyces-derived lasso peptide, RES-701-3, is a selective inhibitor for ETB and a compelling candidate for therapeutic development. However, meager production from a genetically recalcitrant host has limited further structure-activity relationship studies of this potent inhibitor. Here, we report cryo-electron microscopy structures of ETB receptor in both its apo form and complex with RES-701-3, facilitated by a calcineurin-fusion strategy. Hydrophobic interactions between RES-701-3 and the transmembrane region of the receptor, especially involving two tryptophan residues, play a crucial role in RES-701-3 binding. Furthermore, RES-701-3 prevents conformational changes associated with G-protein coupling, explaining its inverse agonist activity. A comparative analysis with other lasso peptides and their target proteins highlights the potential of lasso peptides as precise drug candidates for G-protein-coupled receptors. This structural insight into RES-701-3 binding to ETB receptor offers valuable information for the development of novel therapeutics targeting this receptor and provides a broader understanding of lasso peptide interactions with human cell-surface receptors.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: O.N. is a co-founder and scientific advisor for Curreio. P.A.J., A.L., B.K.O., G.C.M.C., H.M., and M.J.B. are employed by Lassogen Inc. All other authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

