The mechanochemical cycle of reactive full-length human dynein 1
- PMID: 40263469
- PMCID: PMC12350074
- DOI: 10.1038/s41594-025-01543-3
The mechanochemical cycle of reactive full-length human dynein 1
Abstract
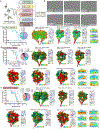
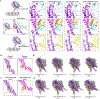
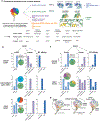
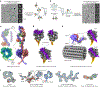
Dynein-driven cargo transport has a pivotal role in diverse cellular activities, central to which is dynein's mechanochemical cycle. Here, we performed a systematic cryo-electron microscopic investigation of the conformational landscape of full-length human dynein 1 in reaction, in various nucleotide conditions, on and off microtubules. Our approach reveals over 40 high-resolution structures, categorized into eight states, providing a dynamic and comprehensive view of dynein throughout its mechanochemical cycle. The described intermediate states reveal mechanistic insights into dynein function, including a 'backdoor' phosphate release model that coordinates linker straightening, how microtubule binding enhances adenosine triphosphatase activity through a two-way communication mechanism and the crosstalk mechanism between AAA1 and the regulatory AAA3 site. Our findings also lead to a revised model for the force-generating powerstroke and reveal means by which dynein exhibits unidirectional stepping. These results improve our understanding of dynein and provide a more complete model of its mechanochemical cycle.
© 2025. The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer Nature America, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures












References
-
- King SM The dynein microtubule motor. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1496, 60–75 (2000). - PubMed
-
- Ricolo D, Castro-Ribera J. & Araujo SJ Cytoskeletal players in single-cell branching morphogenesis. Dev. Biol 477, 22–34 (2021). - PubMed
-
- Klena N. & Pigino G.Structural biology of cilia and intraflagellar transport. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol 38, 103–123 (2022). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

