Efficient control of spider-like medical robots with capsule neural networks and modified spring search algorithm
- PMID: 40263478
- PMCID: PMC12015316
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-025-95288-0
Efficient control of spider-like medical robots with capsule neural networks and modified spring search algorithm
Abstract
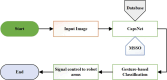
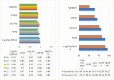
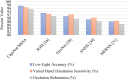
This study introduces an innovative method for gesture recognition in medical robotics, utilizing Capsule Neural Networks (CNNs) in conjunction with the Modified Spring Search Algorithm (MSSA). This approach achieves remarkable efficiency in gesture identification, facilitating precise control over medical robots. The proposed system undergoes thorough evaluation through both simulations and practical experiments, showing its capability to enhance patient outcomes in robotic surgical procedures. The primary contributions of this research include the creation of a unique CNN-MSSA architecture for gesture recognition, an extensive assessment of the system's performance, and evidence of its potential to advance patient care. The findings indicate that the system attains an accuracy rate of 95% with a processing duration of 0.5 s, surpassing existing methodologies. These results carry significant implications for the advancement of autonomous medical robots and the enhancement of patient care in robotic surgery, underscoring the technology's potential to improve the precision and efficiency of medical interventions.
Keywords: Bio-inspired; Capsule neural network; Gesture-based control; MATLAB; Medical applications; Metaheuristic; Modified spring search algorithm; Robots.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Enhancement of surgical hand gesture recognition using a capsule network for a contactless interface in the operating room.Comput Methods Programs Biomed. 2020 Jul;190:105385. doi: 10.1016/j.cmpb.2020.105385. Epub 2020 Feb 6. Comput Methods Programs Biomed. 2020. PMID: 32062090
-
A CNN-based prototype method of unstructured surgical state perception and navigation for an endovascular surgery robot.Med Biol Eng Comput. 2019 Sep;57(9):1875-1887. doi: 10.1007/s11517-019-02002-0. Epub 2019 Jun 20. Med Biol Eng Comput. 2019. PMID: 31222531
-
Finger Gesture Spotting from Long Sequences Based on Multi-Stream Recurrent Neural Networks.Sensors (Basel). 2020 Jan 18;20(2):528. doi: 10.3390/s20020528. Sensors (Basel). 2020. PMID: 31963623 Free PMC article.
-
Image-based laparoscopic tool detection and tracking using convolutional neural networks: a review of the literature.Comput Assist Surg (Abingdon). 2020 Dec;25(1):15-28. doi: 10.1080/24699322.2020.1801842. Comput Assist Surg (Abingdon). 2020. PMID: 32886540 Review.
-
Deep Learning: A Primer for Neurosurgeons.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2024;1462:39-70. doi: 10.1007/978-3-031-64892-2_4. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2024. PMID: 39523259 Review.
References
-
- Aslan, E., Arserim, M. A. & Uçar, A. İnsansı robot robotis-op2 Için Itme Kurtarma kontrol Yöntemlerinin Karşılaştırılması. Gazi Üniversitesi Mühendislik Mimarlık Fakültesi Dergisi39(4), 2551–2566
-
- Kukker, A., Sharma, R. & Malik, H. Forearm movements classification of EMG signals using Hilbert Huang transform and artificial neural networks. In I2016 EEE 7th Power India International Conference (PIICON) 1–6 (IEEE, 2016).
-
- Bhattacharya, P. et al. Demystifying ChatGPT: An In-depth survey of OpenAI’s robust large Language models. Arch. Comput. Methods Eng. 1–44, (2024).
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

