Pemafibrate modulates peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha and prevents alcohol-associated liver disease in rats
- PMID: 40263984
- PMCID: PMC12012945
- DOI: 10.1186/s10020-025-01210-9
Pemafibrate modulates peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha and prevents alcohol-associated liver disease in rats
Abstract
Background and aims: Alcohol-associated liver disease (ALD) with steatosis or steatohepatitis that could progress to liver cirrhosis is a common problem in chronic alcohol consumption. Pemafibrate is a novel, highly specific peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-α (PPARα) modulator, which regulates the expression of the target genes related to lipid and glucose metabolism. Here, we evaluated the effect of pemafibrate to prevent ALD and steatosis in rats.
Methods: The animals were treated with liquid diet containing ethanol (36% of total calories) or an isocaloric carbohydrate diet for 4 weeks. Subsequently, both groups were fed with either 0.5% aqueous methylcellulose solution (MC) or MC containing 0.3 mg/kg body weight of pemafibrate orally twice a day along with the liquid diet for another 4 weeks. A set of animals were sacrificed at the 4th week before the start of pemafibrate treatment and the remaining animals at the end of 8 weeks. Blood and liver samples were collected for biochemical and histopathological evaluations.
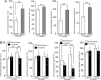
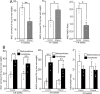
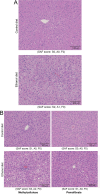
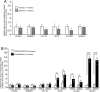
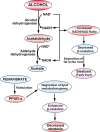
Results: Treatment with pemafibrate prevented inflammation and steatosis in the hepatic tissue. Furthermore, pemafibrate administration markedly increased hepatic NAD and NADH levels, reduced both serum and hepatic triglyceride levels, and upregulated the expression of molecules involved in lipid metabolism.
Conclusions: The results of the present study demonstrated that pemafibrate modulates target genes related to hepatic lipid metabolism and prevents deposition of fat globules in the liver during chronic alcohol feeding in rats. Therefore, pemafibrate could be used as a potent therapeutic agent to prevent steatosis and related adverse events in ALD.
Keywords: Alcohol-associated liver disease; PPARα; Pemafibrate; Steatohepatitis; Steatosis.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: The animal experiments were carried out as per the Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals published by the US National Institutes of Health (NIH Publication No. 86-23, revised 1996). The animal experimental protocol was approved by the Animal Care and Use Committee of Kanazawa Medical University on the Ethics of use and care of experimental animals (#2022-29). Consent for publication: Not applicable. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



References
-
- Bedossa P, Poitou C, Veyrie N, Bouillot JL, Basdevant A, Paradis V, Tordjman J, Clement K. Histopathological algorithm and scoring system for evaluation of liver lesions in morbidly obese patients. Hepatology. 2012;56(5):1751–9. 10.1002/hep.25889. - PubMed
-
- Blair HA. Pemafibrate: first global approval. Drugs. 2017;77(16):1805–10. 10.1007/s40265-017-0818-x. - PubMed
-
- Bougarne N, Weyers B, Desmet SJ, Deckers J, Ray DW, Staels B, De Bosscher K. Molecular actions of PPARα in lipid metabolism and inflammation. Endocr Rev. 2018;39(5):760–802. 10.1210/er.2018-00064. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

