Assessing the interchangeability of keratometry measurements from four biometric devices in intraocular lens power calculations: insights into the predictive accuracy of five modern IOL formulas
- PMID: 40264002
- PMCID: PMC12016114
- DOI: 10.1186/s12886-025-04067-y
Assessing the interchangeability of keratometry measurements from four biometric devices in intraocular lens power calculations: insights into the predictive accuracy of five modern IOL formulas
Abstract
Background: Achieving accurate intraocular lens (IOL) power calculation is crucial for successful refractive outcomes in cataract surgery. This study aimed to evaluate the interchangeability of keratometry (K) values obtained from four biometric devices (IOLMaster 700, CASIA2, Pentacam, and iTrace) and assess the predictive accuracy of five modern IOL calculation formulas (Barrett Universal II, Cooke K6, EVO 2.0, Kane, and PEARL-DGS) when using K values from these different devices.
Methods: This prospective study included K values obtained from four biometric devices for use in five IOL power calculation formulas. Predictive accuracy was assessed using multiple statistical parameters, including standard deviation (SD), mean absolute error (MAE), median absolute error (MedAE) and root mean square absolute error (RMSAE). The interchangeability of devices was evaluated by comparing predictive outcomes across devices and formulas, with statistical analyses focusing on consistency and agreement.
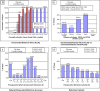
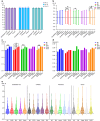
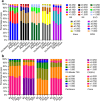
Results: Predictive accuracy across the five IOL formulas was stable and showed no statistically significant differences when using keratometry measurements from the same biometric device. However, significant variability was noted when comparing K values from different devices using the same formula. The SS-OCT-based devices (IOLMaster 700 and CASIA2) showed higher consistency in predictive accuracy compared to Scheimpflug-based Pentacam and ray-tracing-based iTrace. Despite this inter-device variability, all five IOL formulas showed overall robust performance across different devices.
Conclusions: Our findings indicate that keratometry measurements from different biometric devices are not fully interchangeable. SS-OCT-based devices (IOLMaster 700 and CASIA2) provided superior consistency in refractive prediction accuracy. Therefore, clinicians should carefully select biometric device-formula combinations based on the specific measurement principles and desired refractive outcomes. Further research involving larger sample sizes, additional IOL types and biometric devices, as well as assessment of surgeon-related factors, is warranted to optimize refractive accuracy in cataract surgery.
Keywords: Biometric devices; Cataract surgery; IOL power calculation; Keratometry values; Refractive outcomes.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: This prospective study was approved by the Institutional Review Board of the Tianjin Medical University Eye Hospital, Tianjin, China (No.2023KY-04). All procedures adhered to the tenets of the Declaration of Helsinki. All participants provided written informed consent before cataract surgery for the use of their clinical data. Consent for publication: Not Applicable. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Stopyra W. The exactness of intraocular Lens power calculation formulas for short eyes and correlation between method accuracy and eyeball axial length. Cesk Slov Oftalmol. 2022;78(5):236–40. - PubMed
-
- Ma S, Gao R, Sun J, Yang J, Wen K, Chen X, Zhao F, Xu X, Tian F. Comparison of two swept-source optical coherence tomography devices, a Scheimpflug camera system and a ray-tracing aberrometer in the measurement of corneal power in patients with cataract. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2024;262(5):1567–78. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- TJYXZDXK-037A/Tianjin Key Medical Discipline (Specialty) Construction Project
- TJYXZDXK-037A/Tianjin Key Medical Discipline (Specialty) Construction Project
- TJYXZDXK-037A/Tianjin Key Medical Discipline (Specialty) Construction Project
- TJYXZDXK-037A/Tianjin Key Medical Discipline (Specialty) Construction Project
- TJYXZDXK-037A/Tianjin Key Medical Discipline (Specialty) Construction Project
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

