The association between social determinants of health and all-cause, cardiovascular mortality in US rheumatoid arthritis: a cohort study of NHANES
- PMID: 40264100
- PMCID: PMC12012952
- DOI: 10.1186/s12889-025-22706-3
The association between social determinants of health and all-cause, cardiovascular mortality in US rheumatoid arthritis: a cohort study of NHANES
Abstract
Background: Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) imposes a significant burden on healthcare systems. This study investigates the impact of social determinants of health (SDoH) on the prognosis of RA patients, aiming to inform interventions that improve health outcomes.
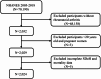
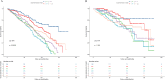
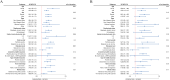
Methods: The National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) 2005-2018 included 2,024 RA participants. SDoH was assessed based on the five domains outlined in the Healthy People 2030 framework, with the cumulative number of adverse SDoH calculated. Cox regression analysis, subgroup analysis, and Kaplan-Meier survival analysis were employed to evaluate the associations between SDoH and all-cause mortality as well as cardiovascular mortality among RA patients, adjusting for potential confounding factors.
Results: Over a median follow-up of 79 months, 449 deaths (19%) occurred, including 120 cardiovascular deaths. Each 1-point increase in cumulative SDoH score was linked to a 24% higher risk of all-cause mortality (HR: 1.24; 95% CI: 1.16-1.32; p < 0.001) and a 25% higher risk of cardiovascular mortality (HR: 1.25; 95% CI: 1.13-1.39; p < 0.001). Exposure to five or more adverse SDoH was associated with a higher risk of all-cause mortality (HR: 3.94; 95% CI: 2.20-7.06; p < 0.001) as well as cardiovascular mortality (HR: 3.98; 95% CI: 1.22-12.97; p = 0.020). Significant interactions were found between SDoH and age, income, and education level.
Conclusion: Adverse SDoH, particularly when accumulated, are associated with increased mortality risks in RA patients, emphasizing the need for targeted interventions to mitigate these effects.
Keywords: All-cause mortality; Cardiovascular mortality; NHANES; Rheumatoid arthritis; Social determinants of health.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: The NHANES are public databases. The patients involved in the database received ethical approval. Users can download relevant data for free for research and publication purposes. Consent for publication: Not applicable. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests. Clinical trial number: Not applicable.
Figures
References
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

