Taurochenodeoxycholic acid suppresses the progression of glioblastoma via HMGCS1/HMGCR/GPX4 signaling pathway in vitro and in vivo
- PMID: 40264142
- PMCID: PMC12016240
- DOI: 10.1186/s12935-025-03782-2
Taurochenodeoxycholic acid suppresses the progression of glioblastoma via HMGCS1/HMGCR/GPX4 signaling pathway in vitro and in vivo
Abstract
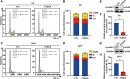
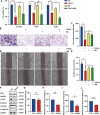
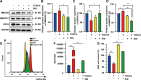
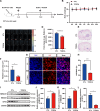
Glioblastoma multiforme (GBM) is the foremost prevalent and highly aggressive intracranial malignancy, which urgently needs safer and more efficacious therapeutic strategies. Our research aimed to investigate the impact and the underlying mechanism of Taurochenodeoxycholic acid (TCDCA) on GBM. In this study, we explored the suppressive effect of TCDCA in vitro by qualification of proliferation and migration assays and flow cytometry, and subsequently predicted the potential anti-GBM mechanism of TCDCA by mRNA sequencing and the following rescue experiments. An orthotopic GBM model in C57BL/6 mice further demonstrated the anti-GBM mechanism of TCDCA. In vitro experiments verified that TCDCA inhibited the growth and migration of GBM cells and induced cell cycle arrest at the G2/M phase. Subsequent mechanism investigations showed that upregulation of HMGCS1 and HMGCR and downregulation of glutathione peroxidase-4 (GPX4) was observed in GBM cells by TCDCA treatment. Notably, inhibitory effects of proliferation and migration as well as induction of ferroptosis by TCDCA were partially restored by Simvastatin (SIN), a competitive HMGCR inhibitor. Furthermore, TCDCA showed an anti-GBM effect in an orthotopic transplantation model in vivo. TCDCA impedes GBM progression by virtue of this intricately orchestrated molecular cascade, through HMGCS1/HMGCR/GPX4 signaling axis, thus unveiling a novel therapeutic avenue warranting further scrutiny in the treatment landscape of GBM.
Keywords: Ferroptosis; Glioblastoma multiforme; HMGCR; Migration; Proliferation; Taurochenodeoxycholic acid.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: The Animal Care and Use Committee at Hangzhou Normal University granted consent to all animal research, and the approval number is HSD20220105. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



References
-
- Wirsching H-G, Galanis E, Weller M. Glioblastoma. In Gliomas. 2016. p. 381–397. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

