Association between the preoperative N-terminal pro-B-type natriuretic peptide and acute kidney injury in gastrointestinal surgery patients managed with enhanced recovery strategy: a retrospective cohort study
- PMID: 40264198
- PMCID: PMC12016297
- DOI: 10.1186/s13741-025-00528-6
Association between the preoperative N-terminal pro-B-type natriuretic peptide and acute kidney injury in gastrointestinal surgery patients managed with enhanced recovery strategy: a retrospective cohort study
Abstract
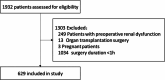
Importance Previous evidence has indicated that N-terminal pro-B-type natriuretic peptide (NT-proBNP) is associated with postoperative acute kidney injury (AKI). However, the association between preoperative NT-proBNP level and postoperative AKI in surgeries managed with enhanced recovery after surgery (ERAS) strategy requires further clarification.Objective To explore the association between preoperative NT-proBNP and the incidence of postoperative AKI in patients who underwent gastrointestinal surgeries and managed with ERAS strategy.Design A retrospective cohort study.Setting A review of documented cases of elective gastrointestinal surgeries managed with ERAS strategy occurred at Xijing Hospital from 01 May 2017 to 30 June 2022.Participants A total of 629 patients aged 18 years or older who were scheduled for elective gastrointestinal surgeries and subjected to the ERAS strategy with preoperative NT-proBNP and creatinine measurements were included in the analysis.Exposure Preoperative serum concentrations of NT-proBNP.Main outcomes and measures The primary outcome was the incidence of postoperative AKI. Preoperative NT-proBNP was divided into high- or low-level groups based on the median (165 pg/ml). Logistic regression was used to explore the association between increased preoperative NT-proBNP level and risk of AKI.Results After screening 1932 case records, 629 cases were included in the final analyses. The average age was 63.5 (15.3) years old and 197 (31.3%) of them were female. Among them, 112 (17.8%) developed postoperative AKI. The incidence of AKI was 21% in the high NT-proBNP group, and 14.6% in the low NT-proBNP group. Patients with higher preoperative NT-proBNP levels (≥ 165 pg/mL) have significant higher risk of postoperative AKI as compared to those in the lower group (adjusted OR 1.75; 95% CI 1.12 to 2.73).Conclusions and relevance Increased preoperative NT-proBNP is associated with an elevated risk of postoperative AKI in patients who underwent gastrointestinal surgery and managed with ERAS strategy.Trial registry number Clinical trial registry number: NCT06145347.
Keywords: ERAS; Gastrointestinal surgery; Postoperative AKI; Preoperative NT-proBNP.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: This study was approved by KY- 20232265-F- 1 from Approval Form I E C of our hospital. The need for written informed consent was waived, because of the study’s retrospective nature. Consent for publication: All authors approved the final manuscript and the submission to this journal. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Preoperative NT-proBNP and LVEF for the prediction of acute kidney injury after noncardiac surgery: a single-centre retrospective study.BMC Anesthesiol. 2022 Jun 24;22(1):196. doi: 10.1186/s12871-022-01727-0. BMC Anesthesiol. 2022. PMID: 35751021 Free PMC article.
-
Prediction of acute kidney injury after cardiac surgery from preoperative N-terminal pro-B-type natriuretic peptide.Br J Anaesth. 2021 Dec;127(6):862-870. doi: 10.1016/j.bja.2021.08.015. Epub 2021 Sep 22. Br J Anaesth. 2021. PMID: 34561052
-
Predictive value of perioperative NT-proBNP levels for acute kidney injury in patients with compromised renal function undergoing cardiac surgery: a case control study.BMC Anesthesiol. 2024 Aug 28;24(1):298. doi: 10.1186/s12871-024-02672-w. BMC Anesthesiol. 2024. PMID: 39198720 Free PMC article.
-
Predictive value of systemic immune-inflammation index combined with N-terminal pro-brain natriuretic peptide for contrast-induced acute kidney injury in patients with STEMI after primary PCI.Int Urol Nephrol. 2024 Mar;56(3):1147-1156. doi: 10.1007/s11255-023-03762-3. Epub 2023 Sep 2. Int Urol Nephrol. 2024. PMID: 37658947
-
Diagnostic accuracy of NT-proBNP to predict the incidence of CSA-AKI: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Medicine (Baltimore). 2024 Oct 25;103(43):e39479. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000039479. Medicine (Baltimore). 2024. PMID: 39470551 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Agha R, Abdall-Razak A, Crossley E, et al. STROCSS 2019 guideline: strengthening the reporting of cohort studies in surgery. Int J Surg. 2019;72:156–65. - PubMed
-
- Andreucci M, Federico S, Andreucci VE. Edema and acute renal failure. Semin Nephrol. 2001;21(3):251–6. - PubMed
-
- Berri RN, Sahai SK, Durand JB, et al. Serum brain naturietic peptide measurements reflect fluid balance after pancreatectomy. J Am Coll Surg. 2012;214(5):778–87. - PubMed
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

