Human γδ T Cell Function Is Impaired Upon Mevalonate Pathway Inhibition
- PMID: 40264329
- PMCID: PMC12130672
- DOI: 10.1111/imm.13931
Human γδ T Cell Function Is Impaired Upon Mevalonate Pathway Inhibition
Abstract
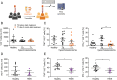
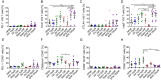
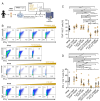
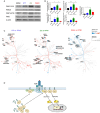
Vδ2 T cells, a predominant human peripheral γδ T cell population, are a promising candidate for the development of immunotherapies against cancer and infected cells. Aminobisphosphonate drugs, such as zoledronate, are commonly used to expand Vδ2 T cells. Yet, such in vitro generated cells have limited efficacy in the clinic. We found that despite inducing excessive proliferation of Vδ2 T cells, zoledronate impaired their effector function and caused the upregulation of the inhibitory receptor TIM3. This effect was due to the inhibition of mevalonate metabolism and dysregulation of downstream biological processes such as protein prenylation and intracellular signalling. In vitro and in vivo inhibition of mevalonate metabolism with zoledronate, statins, and 6-fluoromevalonate, as well as genetic deficiency of the mevalonate kinase, all resulted in compromised cytokine and cytotoxic molecule production by Vδ2 T cells. Impaired Vδ2 T cell function was accompanied by transcriptome and kinome changes. Our findings reveal the importance of mevalonate metabolism for the proper functioning of Vδ2 T cells. This observation provides important considerations for improving their therapeutic use and has repercussions for patients with statin or aminobisphosphonate treatments.
Keywords: T cell; cytokines; flow cytometry; human; protein kinases/phophatases.
© 2025 The Author(s). Immunology published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
L.A.B.J. and M.G.N. are scientific founders of TTxD and Lemba. The other authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Puan K. J., Jin C., Wang H., et al., “Preferential Recognition of a Microbial Metabolite by Human V 2V 2 T Cells,” International Immunology 19, no. 5 (March 2007): 657–673. - PubMed
-
- Eberl M., Hintz M., Reichenberg A., Kollas A. K., Wiesner J., and Jomaa H., “Microbial Isoprenoid Biosynthesis and Human γδ T Cell Activation,” FEBS Letters 544, no. 1–3 (June 2003): 4–10. - PubMed
-
- Morita C. T., Jin C., Sarikonda G., and Wang H., “Nonpeptide Antigens, Presentation Mechanisms, and Immunological Memory of Human Vγ2Vδ2 T Cells: Discriminating Friend From Foe Through the Recognition of Prenyl Pyrophosphate Antigens,” Immunological Reviews 215, no. 1 (February 2007): 59–76. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- CVON2018-27/Dutch HEart Foundation/Dutch Cardiovascular Alliance
- 390873048/German Research Foundation (DFG), the grant number is EXC2151/1 ImmunoSensation2-the Immune Sensory System
- SFB1454/German Research Foundation (DFG)
- 798582/European Comission" the program is "Horizon 2020 Research and Innovation Program Under the MArie Sklodowska-Curie
- 502/19-3/German Research Foundation (DFG)
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

