Alzheimer's disease and insomnia: a bibliometric study and visualization analysis
- PMID: 40264463
- PMCID: PMC12011777
- DOI: 10.3389/fnagi.2025.1542607
Alzheimer's disease and insomnia: a bibliometric study and visualization analysis
Abstract
Background: Alzheimer's disease (AD) is the fastest-growing neurodegenerative disorder globally, with patient numbers expected to rise to 130 million by 2050. Insomnia, a prevalent comorbidity, exhibits a bidirectional relationship with AD: insomnia accelerates AD pathology, while AD worsens sleep disorders. This relationship has emerged as a key area of research. Current mechanisms involve oxidative stress, inflammatory responses, and glymphatic system dysfunction, yet a comprehensive review of these processes remains absent.
Objective: To conduct a visual analysis of the relationship between Alzheimer's disease and insomnia using CiteSpace.
Methods: Literature on "insomnia" and "Alzheimer's disease" published between January 1, 2000, and October 31, 2024, was retrieved from the Web of Science Core Collection. CiteSpace and VOSviewer software were used to analyze institutions, authors, and keywords.
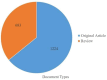
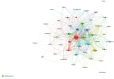
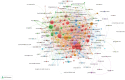
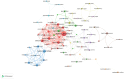
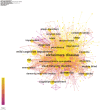
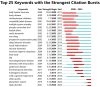
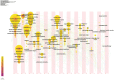
Results: A total of 1,907 articles were analyzed, revealing a consistent upward trend in publication volume. The United States and the Mayo Clinic were identified as leading contributors, producing 704 and 57 publications, respectively. Boeve Bradley F the most prolific author contributed 30 publications. Collaboration was actively observed among countries, institutions, and authors. High-frequency keywords identified were "Parkinson's disease," "cognitive impairment," and "sleep behavior disorder." Emerging research areas are likely to focus on "sleep quality" and the "glymphatic system."
Conclusion: This study is the first to apply bibliometric analysis to identify three key trends in AD and insomnia research: the dominance of the United States and Mayo Clinic, strong international collaboration, and a focus on critical areas such as cognitive impairment, the glymphatic system, and sleep interventions. Insomnia may accelerate AD progression via multiple pathways, indicating that enhancing sleep quality could provide new strategies for early intervention. Future research should prioritize advancing the clinical translation of sleep interventions and investigating the mechanisms of the glymphatic system.
Keywords: Alzheimer's disease; CiteSpace; VOSviewer; bibliometrics; insomnia; visual analysis.
Copyright © 2025 Tian, Jiang, Jin, Yu, Chen and Wang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest. The reviewer WZ declared a shared affiliation with the authors MJ, X-KY to the handling editor at the time of review.
Figures


References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

