Efficacy and safety of programmed cell death protein-1 inhibitor for first-line therapy of advanced gastric or gastroesophageal junction cancer: a network meta-analysis
- PMID: 40264761
- PMCID: PMC12011870
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1500954
Efficacy and safety of programmed cell death protein-1 inhibitor for first-line therapy of advanced gastric or gastroesophageal junction cancer: a network meta-analysis
Abstract
Background: This study conducted a network meta-analysis to evaluate and rank the safety and efficacy of programmed cell death protein-1 (PD-1) inhibitors for patients with advanced gastric or gastroesophageal junction cancer (GC/GEJC).
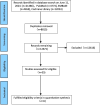
Methods: A systematic search was conducted in PubMed, Embase, and Cochrane Library databases to compare the efficacy and safety of different treatment regimens, including overall survival (OS), progression-free survival (PFS), objective response rate (ORR), and treatment-related adverse events (TRAEs) in patients with advanced GC/GEJC.
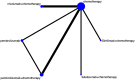
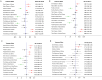
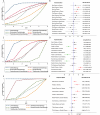
Results: A total of six RCT studies were ultimately included in the analysis, involving 6,294 patients. Among them, 256 patients received PD-1 inhibitor monotherapy (pembrolizumab), 3,029 patients received a PD-1 inhibitor plus chemotherapy (1,047 with pembrolizumab, 1,154 with nivolumab, 327 with sintilimab, and 501 with tislelizumab), and 3,009 received either chemotherapy or chemotherapy plus placebo. Sintilimab plus chemotherapy had the highest SUCRA value for OS (85.2%), while nivolumab plus chemotherapy had the highest SUCRA values for both PFS and ORR (96.8% and 82.9%). Four PD-1 inhibitors plus chemotherapy significantly improved median OS and ORR compared with chemotherapy. Sintilimab plus chemotherapy, pembrolizumab plus chemotherapy, and nivolumab plus chemotherapy significantly improved median PFS compared with chemotherapy. For TRAEs of grade 3 or worse, pembrolizumab monotherapy had the highest SUCRA value. Tislelizumab plus chemotherapy, as well as sintilimab plus chemotherapy, did not increase the overall incidence of TRAEs and the incidence of grade 3 or worse TRAEs.
Conclusions: In the first-line treatment of advanced GC/GEJC, PD-1 inhibitors plus chemotherapy have been demonstrated to significantly improve OS, PFS, and ORR compared with chemotherapy. Among them, sintilimab plus chemotherapy achieved the highest SUCRA value for OS, and nivolumab plus chemotherapy achieved the highest SUCRA values for PFS and ORR. Regarding safety, tislelizumab plus chemotherapy and sintilimab plus chemotherapy did not increase the overall incidence of TRAEs and the incidence of grade 3 or worse TRAEs, with good tolerability and safety.
Keywords: PD-1 inhibitor; advanced gastric cancer; first-line treatment; gastroesophageal junction cancer; network meta-analysis.
Copyright © 2025 Zhang, Peng, Yang, Zhang and Fan.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
The efficacy and safety of PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitors in combination with chemotherapy as a first-line treatment for unresectable, locally advanced, HER2-negative gastric or gastroesophageal junction cancer: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials.Front Immunol. 2025 Mar 26;16:1566939. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1566939. eCollection 2025. Front Immunol. 2025. PMID: 40207218 Free PMC article.
-
The efficacy and safety of PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitors plus chemotherapy versus chemotherapy alone in advanced or metastatic gastric or gastroesophageal junction cancer: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials.Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 2025 Aug;81(8):1129-1139. doi: 10.1007/s00228-025-03861-3. Epub 2025 Jun 10. Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40493058 Review.
-
Efficacy and safety of pembrolizumab in advanced gastric and gastroesophageal junction cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis.BMC Gastroenterol. 2025 Mar 14;25(1):173. doi: 10.1186/s12876-025-03754-w. BMC Gastroenterol. 2025. PMID: 40087572 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy and safety of PD-1 inhibitors as second-line treatment for advanced squamous esophageal cancer: a systematic review and network meta-analysis with a focus on PD-L1 expression levels.Front Immunol. 2025 Jan 23;15:1510145. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1510145. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2025. PMID: 39916953 Free PMC article.
-
Safety and efficacy of pembrolizumab in combination with S-1 plus oxaliplatin as a first-line treatment in patients with advanced gastric/gastroesophageal junction cancer: Cohort 1 data from the KEYNOTE-659 phase IIb study.Eur J Cancer. 2020 Apr;129:97-106. doi: 10.1016/j.ejca.2020.02.002. Epub 2020 Mar 4. Eur J Cancer. 2020. PMID: 32145474 Clinical Trial.
References
-
- Janjigian YY, Ajani JA, Moehler M, Shen L, Garrido M, Gallardo C, et al. . First-line nivolumab plus chemotherapy for advanced gastric, gastroesophageal junction, and esophageal adenocarcinoma: 3-year follow-up of the phase III checkmate 649 trial. J Clin Oncol. (2024) 42:2012–20. doi: 10.1200/jco.23.01601 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

