Peripheral biological correlates of suicidality in children and adolescents: A systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 40264798
- PMCID: PMC12013498
- DOI: 10.1016/j.isci.2025.112290
Peripheral biological correlates of suicidality in children and adolescents: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
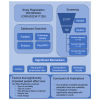
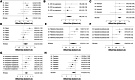
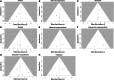
A systematic review and meta-analysis were conducted to identify peripheral biological correlates of suicidality in children and adolescents. The review was pre-registered through PROSPERO (CRD42023417128) and included four databases (PubMed, Cochrane Library, Embase, and PsycINFO). From 27,977 non-duplicated articles, 102 full-text studies were selected. Studies investigated suicide attempts (n = 52), suicidal ideation (n = 42), or individuals with suicidal ideation or attempts grouped together (n = 22). Seropositive toxoplasmosis, cortisol, neutrophil, and neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio (NLR) exhibited significant effect size after Bonferroni correction. Effect sizes for biological correlates of suicidality were pooled using Cohen's d (effect size = -0.04, 95% confidence interval [CI]: -1.36 to 1.27) and odds ratio (effect size = -0.31, 95% CI: -1.06 to 0.42). Meta-regression analysis revealed that type of suicidality, type of control, means collected, and sample size significantly impacted the pooled effect size. Analysis showed significant publication bias and heterogeneity, as well as notable moderators and potential biomarkers for future research.
Keywords: Psychology; Public health.
© 2025 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
T.K.P., E.R.A., D.C., L.J., Z.F., and A.N. report no conflicts of interest. G.E. is a consultant for Lundbeck and Neuronetics. G.E. receives research support from American Foundation for Suicide Prevention (AFSP), Janssen Pharmaceuticals, Janssen Research & Development, the National Institutes of Health, Patient-Centered Outcomes Research Institute (PCORI), and the State of Texas. M.H.T. has received research funding from NIMH, NIDA, NCATS, the American Foundation for Suicide Prevention, the Patient-Centered Outcomes Research Institute, and the Blue Cross Blue Shield of Texas. He has served as a consultant or advisor for ACADIA PHARMACEUTICALS INC., Akili Interactive, ALKERMES INC (Pub Steering Comm-ALKS5461), Allergan Sales LLC, Alto Neuroscience, Inc. , Applied Clinical Intelligence, LLC (ACI), Axome Therapeutics, Boehringer Ingelheim, Engage Health Media, Gh Research, GreenLight VitalSign6, Inc., Heading Health, Inc., Health Care Global Village, Janssen – Cilag.SA, Janssen Research and Development, LLC (Adv Committee Esketamine), Janssen Research and Development, LLC (panel for study design for MDD relapse), Janssen - ORBIT, Legion Health, Jazz Pharmaceuticals, LUNDBECK RESEARCH U.S.A, Medscape, LLC, Merck Sharp & Dohme Corp., Mind Medicine (MindMed) Inc., Myriad Neuroscience, Neurocrine Biosciences Inc, Navitor, Pharmaceuticals, Inc., Noema Pharma AG, Orexo US Inc., Otsuka Pharmaceutical Development & Commercialization, Inc. (PsychU, MDD Section Advisor), Otsuka America Pharmaceutical, Inc. (MDD expert), Pax Neuroscience, Perception Neuroscience Holdings, Inc., Pharmerit International, LP, Policy Analysis Inc., Sage, Therapeutics, Rexahn Pharmaceuticals, Inc., Sage Therapeutics, Signant Health, SK Life Science, Inc., Takeda Development Center Americas, Inc., The Baldwin Group, Inc., and Titan Pharmaceuticals, Inc. M.H.T. also received editorial compensation from Oxford University Press. Disclaimer: The Intellectual Property of VitalSign6 belongs to the University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center (Principal Investigator, M.H.T.) and is now licensed to GLVS6 for future distribution.
Figures

References
-
- Curtin S.C., Tejada-Vera B., Bastian B.A. Deaths: Leading Causes for 2020. Natl. Vital Stat. Rep. 2023;72:1–115. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

