Heme Oxygenase-1 Modulates Macrophage Polarization Through Endothelial Exosomal miR-184-3p and Reduces Sepsis-Induce Lung Injury
- PMID: 40264818
- PMCID: PMC12013636
- DOI: 10.2147/IJN.S506830
Heme Oxygenase-1 Modulates Macrophage Polarization Through Endothelial Exosomal miR-184-3p and Reduces Sepsis-Induce Lung Injury
Abstract
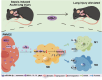
Introduction: Pulmonary microvascular endothelial cells (PMVECs) are notably implicated in the pathogenesis of sepsis-induced lung injury. Exosomes derived from PMVECs facilitate intercellular communication among various cell types, especially crosstalk with macrophages. Heme oxygenase-1 (HO-1), an early stress-responsive enzyme with inherent protective functions, has been implicated in acute lung injury (ALI) mitigation. But research on the mechanism of HO-1 in macrophage polarization via PMVEC exosomes in sepsis-induced lung injury is lacking.
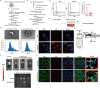
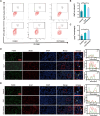
Methods: To investigate the role of HO-1 in the interaction between endothelial cells and macrophages, HO-1 knockout mouse model were established. Exosomes from PMVECs were isolated, and differential expression of microRNA (miRNA) was determined by sequencing. An in vitro co-culture system involving Murine Alveolar Macrophage Cell Line (MH-S cells) and HO-1/ PMVECs-derived exosomes (HP-exos) was used to investigate the underlying mechanisms. To further verify the involvement of HO-1 in intercellular communication through exosomal miRNA in vivo, the level of pulmonary inflammation was evaluated, and the polarization of pulmonary macrophages was analyzed.
Results: The results showed that miR-184-3p was significantly downregulated in HP-exos, and supplementation of miR-184-3p enhanced the polarization of M1 macrophages, thus intensifying lung inflammation. HO-1 regulates the polarization of macrophages by regulating endothelial exosomes. Overexpression of HO-1 downregulates miR-184-3p, which negatively regulates Semaphorin 7A (Sema7a), which attenuated M1 type macrophages (M1) polarization and augmented M2 type macrophages (M2) polarization, thereby partially mitigating lung injury and inflammation.
Conclusion: Collectively, we elucidated a novel potential therapeutic mechanism that HO-1 alleviate inflammation by modulating the M1/M2 ratio in sepsis-induced ALI by regulating miR-184-3p/Sema7a expression.
Keywords: MiRNA; acute lung injury; exosome; macrophage polarization; sepsis.
© 2025 Chen et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The author(s) report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Exosomes Derived From Alveolar Epithelial Cells Promote Alveolar Macrophage Activation Mediated by miR-92a-3p in Sepsis-Induced Acute Lung Injury.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2021 May 10;11:646546. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2021.646546. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2021. PMID: 34041043 Free PMC article.
-
Enhanced itaconic acid secretion from macrophages mediates the protection of mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes on lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury mice.Biol Direct. 2024 Dec 26;19(1):138. doi: 10.1186/s13062-024-00586-8. Biol Direct. 2024. PMID: 39721998 Free PMC article.
-
hnRNPA2B1 promotes the production of exosomal miR-103-3p from endothelial progenitor cells to alleviate macrophage M1 polarization in acute respiratory distress syndrome.Int Immunopharmacol. 2025 Jun 17;158:114830. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2025.114830. Epub 2025 May 17. Int Immunopharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40381491
-
Macrophages in sepsis-induced acute lung injury: exosomal modulation and therapeutic potential.Front Immunol. 2025 Jan 7;15:1518008. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1518008. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2025. PMID: 39840035 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Exosomes and MicroRNAs: key modulators of macrophage polarization in sepsis pathophysiology.Eur J Med Res. 2025 Apr 17;30(1):298. doi: 10.1186/s40001-025-02561-z. Eur J Med Res. 2025. PMID: 40247413 Free PMC article. Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

