Evaluation of Clinical Symptoms of Unilateral S1 Nerve Injury Caused by Disc Herniation the via High Resolution MRI and DTI
- PMID: 40264909
- PMCID: PMC12013630
- DOI: 10.2147/JPR.S507867
Evaluation of Clinical Symptoms of Unilateral S1 Nerve Injury Caused by Disc Herniation the via High Resolution MRI and DTI
Abstract
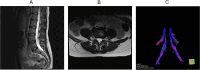
Background: The status of the herniated disc or nucleus pulposus and the extent of injury and clinical symptoms of the compressed S1 nerve fiber bundle were evaluated by high-resolution Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and Diffusion tensor imaging (DTI) techniques.
Methods: Forty-two clinically proven patients with unilateral S1 nerve root compression were selected as the case group (n=42), and 20 healthy volunteers were selected as the control group (n=20). The general data, MRI features and DTI parameters were compared between groups. The effective indicators of S1 neurologic fiber bundle damage were screened by univariate logistic regression analysis and receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve, and multi-factor logistic regression models were constructed to analyze the diagnostic efficiency of each model.
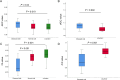
Results: There were no significant differences in age, gender, height, weight, fractional anisotropy (FA) value and apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) value on both sides of S1 nerve root between groups (P >0.05). The FA value and ADC value of the nerve root on the affected side of the patient were significantly different from those on the healthy side and those on the corresponding side of the control group (all P <0.05), and all of them were effective indicators of the damage of S1 nerve. The sensitivity, specificity and area under the curve of the damaged nerve fiber bundle were detected by multi-factor logistic regression models constructed with FA+rFA and FA+rFA+rADC of the affected nerve root, respectively 95.20%, 72.00%, 0.939, and 97.60%, 80.00%, 0.944.
Conclusion: High-resolution MRI and DTI can quantitatively evaluate the degree of nerve fiber bundle injury and clinical symptoms caused by lumbar disc herniation.
Keywords: DTI; apparent diffusion coefficient; fractional anisotropy; high-resolution MRI; lumbar disc herniation.
© 2025 Zhang et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Quantitative Evaluation of the Compressed L5 and S1 Nerve Roots in Unilateral Lumbar Disc Herniation by Using Diffusion Tensor Imaging.Clin Neuroradiol. 2018 Dec;28(4):529-537. doi: 10.1007/s00062-017-0621-9. Epub 2017 Aug 21. Clin Neuroradiol. 2018. PMID: 28828579
-
3.0T MRI tractography of lumbar nerve roots in disc herniation.Acta Radiol. 2014 Oct;55(8):969-75. doi: 10.1177/0284185113508179. Epub 2013 Oct 16. Acta Radiol. 2014. PMID: 24132770
-
Application of Magnetic Resonance Diffusion Tensor Imaging in Diagnosis of Lumbosacral Nerve Root Compression.Curr Med Imaging. 2024;20:e120623217889. doi: 10.2174/1573405620666230612122725. Curr Med Imaging. 2024. PMID: 37309765
-
Diffusion tensor imaging with fiber tracking provides a valuable quantitative and clinical evaluation for compressed lumbosacral nerve roots: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Eur Spine J. 2021 Apr;30(4):818-828. doi: 10.1007/s00586-020-06556-8. Epub 2020 Aug 3. Eur Spine J. 2021. PMID: 32748258
-
Clinical Value and Reliability of Quantitative Assessments of Lumbosacral Nerve Root Using Diffusion Tensor and Diffusion Weighted MR Imaging: A Systematic Review.J Magn Reson Imaging. 2024 Nov;60(5):1823-1839. doi: 10.1002/jmri.29213. Epub 2024 Jan 8. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2024. PMID: 38190195
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

