A New Composite Integrative and Conjugative Element Mediates Multiple Drug Resistance from Streptococcus anginosus to Streptococcus agalactiae
- PMID: 40264923
- PMCID: PMC12013645
- DOI: 10.2147/IDR.S514281
A New Composite Integrative and Conjugative Element Mediates Multiple Drug Resistance from Streptococcus anginosus to Streptococcus agalactiae
Abstract
Introduction: Integrative and conjugative elements (ICEs) are a category of horizontal mobile genetic elements (MGEs) that play important roles in mediating the spread of antimicrobial resistance in Streptococci.
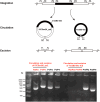
Methods: In this study, a novel ICE, namely ICESan26_rplL, was identified from commensal Streptococcus anginosus through routine silico analyses. The genetic characterization of ICESan26_rplL was explored based on a comparison with known ICEs. The cyclization and cross-species transferability (from Streptococcus anginosus to Streptococcus agalactiae) of ICESan26_rplL were explored using inverse PCR and conjugation transfer experiments.
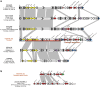
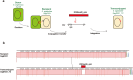
Results: ICESan26_rplL is 61.618 kb in length at downstream of rplL and carries multiple antibiotic resistance genes, including erm(B) [for erythromycin, clindamycin, and streptococcin B (MLSB)], tetM-tetL (tetracycline), lnu and lsa(E) (clindamycin), and ant(6)-I (aminoglycosides). The comparative analysis results showed that ICESan26_rplL was a composite ICE with a mosaic structure composed of modules in the ICESa2603 and TnGBS families. The inverse PCR results demonstrated that ICESan26_rplL could be excised from the chromosome to form a circular intermediate. The conjugation transfer experiment and sequencing results confirmed the cross-species transfer of ICESan26_rplL to S. agalactiae recipients at a relatively low frequency (2.13 × 10-8). Moreover, core functional modules were retrieved from GenBank to search for any ICEs related to ICESan26_rplL. Eventually, 53 putative ICEs were identified, including three composite ICEs with high similarity to ICESan26_rplL, three ICEs in the TnGBS family, and 47 ICEs in the ICESa2603 family.
Discussion: In this study, a novel mosaic ICE was reported for the first time. In addition, its transfer to the major pathogen Streptococcus agalactiae was characterized and proved. These findings suggest that this ICE is expected to become a vehicle for the dissemination of multiple antimicrobial resistance through the wider pathogen Streptococci.
Keywords: ICEs; Streptococcus agalactiae; Streptococcus anginosus; antibiotic resistance genes; composite; conjugation transfer.
© 2025 Wang et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no competing interests in this work.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Comparative Genomic Analysis of the ICESa2603 Family ICEs and Spread of erm(B)- and tet(O)-Carrying Transferable 89K-Subtype ICEs in Swine and Bovine Isolates in China.Front Microbiol. 2016 Feb 2;7:55. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2016.00055. eCollection 2016. Front Microbiol. 2016. PMID: 26870017 Free PMC article.
-
Evolution and Diversity of the Antimicrobial Resistance Associated Mobilome in Streptococcus suis: A Probable Mobile Genetic Elements Reservoir for Other Streptococci.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2016 Oct 7;6:118. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2016.00118. eCollection 2016. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2016. PMID: 27774436 Free PMC article.
-
Diversity and Evolution of the Mobilome Associated with Antibiotic Resistance Genes in Streptococcus anginosus.Microb Drug Resist. 2025 Feb;31(2):52-63. doi: 10.1089/mdr.2024.0229. Epub 2025 Jan 21. Microb Drug Resist. 2025. PMID: 39837262
-
Detection and classification of the integrative conjugative elements of Lactococcus lactis.BMC Genomics. 2024 Apr 1;25(1):324. doi: 10.1186/s12864-024-10255-9. BMC Genomics. 2024. PMID: 38561675 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Role of Integrative and Conjugative Elements in Antibiotic Resistance Evolution.Trends Microbiol. 2021 Jan;29(1):8-18. doi: 10.1016/j.tim.2020.05.011. Epub 2020 Jun 11. Trends Microbiol. 2021. PMID: 32536522 Review.
References
-
- Jensen A, Hoshino T, Kilian M. Taxonomy of the anginosus group of the genus streptococcus and description of Streptococcus anginosus subsp. whileyi subsp. nov. and streptococcus constellatus subsp. viborgensis subsp. nov. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol. 2013;63(Pt 7):2506–2519. doi:10.1099/ijs.0.043232-0 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

