Exploring efficacy of spiritual-based interventions (SBIs) in addressing depressive symptoms among cardiac patients in MENA region: a scoping review
- PMID: 40265003
- PMCID: PMC12012580
- DOI: 10.3389/fpsyg.2025.1552678
Exploring efficacy of spiritual-based interventions (SBIs) in addressing depressive symptoms among cardiac patients in MENA region: a scoping review
Abstract
Background: Depression is a widespread psychological issue among patients with cardiac diseases, which affects treatment adherence, recovery, and overall quality of life. Spiritual-based interventions (SBIs) have gained attention for their potential to alleviate depressive symptoms. However, there is a dearth of research investigating the efficacy of these interventions in the Middle East and North Africa (MENA) region.
Objective: This scoping review aims to synthesize available evidence on the efficacy of spiritual-based interventions in reducing depressive symptoms among cardiac patients in the MENA region.
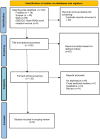
Methods: The present research used a systematic approach to searching electronic databases such as SCOPUS, Web of Science, and ESBECOhost Arab research world in the English language from 2015 to 2025, based on the Arksey and O'Malley framework. Papers were identified based on spiritual-based Intervention addressing depressive symptoms among cardiac patients in the MENA region. Studies were analyzed using the Population-Concept-Context (PCC) framework, as outlined in the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses for Scoping Reviews (PRISMA-ScR).
Results: The analysis pinpoints numerous Spiritual Interventions, such as prayer, mindfulness, and Faith-based counseling, as usual practices. The results showed that SBIs are related to a decrease in depression symptomology and enhancement of psychological wellbeing. Nevertheless, variability in the study models, small amounts of samples, and sparse long-term studies are also some of the current study's limitations.
Conclusion: This research indicates that the efficacy of spiritual-based interventions can reduce depressive signs in cardiac patients in the MENA region. However, additional research is required to ascertain long-term efficacy and cross-cultural effectiveness.
Keywords: MENA region; cardiac patients; depressive symptoms; scoping review; spiritual-based interventions.
Copyright © 2025 Amin.
Conflict of interest statement
The author declares that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest. The author(s) declared that they were an editorial board member of Frontiers, at the time of submission. This had no impact on the peer review process and the final decision.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Beyond the black stump: rapid reviews of health research issues affecting regional, rural and remote Australia.Med J Aust. 2020 Dec;213 Suppl 11:S3-S32.e1. doi: 10.5694/mja2.50881. Med J Aust. 2020. PMID: 33314144
-
Prevalence of type 2 diabetes, prediabetes, and gestational diabetes mellitus in women of childbearing age in Middle East and North Africa, 2000-2017: protocol for two systematic reviews and meta-analyses.Syst Rev. 2018 Jul 18;7(1):96. doi: 10.1186/s13643-018-0763-0. Syst Rev. 2018. PMID: 30021654 Free PMC article.
-
Patient-centered care in the Middle East and North African region: a systematic literature review.BMC Health Serv Res. 2023 Feb 9;23(1):135. doi: 10.1186/s12913-023-09132-0. BMC Health Serv Res. 2023. PMID: 36759898 Free PMC article.
-
The Use of Mobile Technologies to Promote Physical Activity and Reduce Sedentary Behaviors in the Middle East and North Africa Region: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.J Med Internet Res. 2024 Mar 19;26:e53651. doi: 10.2196/53651. J Med Internet Res. 2024. PMID: 38502160 Free PMC article.
-
Psychosocial interventions for preventing and treating depression in dialysis patients.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2019 Dec 2;12(12):CD004542. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD004542.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2019. PMID: 31789430 Free PMC article.
References
-
- AbuRuz M. E., Othman E. H., Al-Dweik G., Momani A., Ahmed F. R. (2023). The effect of holy quran audio therapy on depression and anxiety among jordanian patients following CABG: a randomized control trial. Open Nurs. J. 17:9430510. 10.2174/0118744346262682230921094004 - DOI
-
- Amjadian M., Bahrami Ehsan H., Saboni K., Vahedi S., Rostami R., Roshani D. (2020). A pilot randomized controlled trial to assess the effect of Islamic spiritual intervention and of breathing technique with heart rate variability feedback on anxiety, depression and psycho-physiologic coherence in patients after coronary artery bypass surgery. Ann. Gen. Psychiatry 19:46. 10.1186/s12991-020-00296-1 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials