Analysis of clinical factors and inflammatory cytokines in patients with lung cancer and sarcopenia: a prospective single-center cohort study
- PMID: 40265008
- PMCID: PMC12011579
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2025.1564399
Analysis of clinical factors and inflammatory cytokines in patients with lung cancer and sarcopenia: a prospective single-center cohort study
Abstract
Objective: To analyze the relationship between the expression of various clinical factors, inflammatory cytokines, and sarcopenia and provide new ideas for whole-course management and curative effect prediction in patients with lung cancer and sarcopenia.
Methods: A total of 135 patients with lung cancer recruited in the Department of Oncology, Central Hospital of Shaoyang, from January 2022 to January 2024 were analyzed and divided into sarcopenia (75 cases) and non-sarcopenia (60 cases) groups. Various statistical analyses methods were used to analyze the correlation between 4 kinds of inflammatory cytokines and sarcopenia in patients with lung cancer.
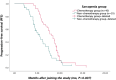
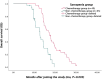
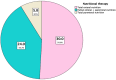
Results: In this study, 55.6% (75/135) of the lung cancer patients were found to have sarcopenia, with a median age of 67.3 years. Those with sarcopenia were found to be significantly associated with increased age, long duration of cigarette inhalation, and high risk of malnutrition. The results of the regression analysis indicated that long-term cigarette inhalation (odds ratio [OR]=8.187), body mass index (BMI; OR=1.356), and Nutritional Risk Screening 2002 score (OR=0.050) were statistically significant (P<0.05). Multivariable logistic regression analysis indicated that patients in the sarcopenia group were positively correlated with interleukin (IL)-6 and tumour necrosis factor (TNF)-α (P<0.05). The progression-free and overall survival of lung cancer patients with sarcopenia who received chemotherapy were significantly increased compared to those who did not receive chemotherapy(P<0.05).
Conclusions: Patients with a long-term cigarette inhalation, high risk of malnutrition, and low BMI have a higher probability of sarcopenia. The increased expression levels of IL-6 are positively correlated with the occurrence of sarcopenia, as well as TNF-α. The intervention of chemotherapy affects inflammatory cytokine levels. Early chemotherapy may extend the survival time of patients with lung cancer and sarcopenia.
Keywords: cytokines; lung cancer; malnutrition; prognosis; sarcopenia.
Copyright © 2025 Liu, Zhang, Chen and Liu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Measurement of sarcopenia in lung cancer inpatients and its association with frailty, nutritional risk, and malnutrition.Front Nutr. 2023 Apr 17;10:1143213. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2023.1143213. eCollection 2023. Front Nutr. 2023. PMID: 37139454 Free PMC article.
-
A study on relationship between elderly sarcopenia and inflammatory factors IL-6 and TNF-α.Eur J Med Res. 2017 Jul 12;22(1):25. doi: 10.1186/s40001-017-0266-9. Eur J Med Res. 2017. PMID: 28701179 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of nutritional indices and inflammatory parameters on patients received immunotherapy for non-small cell lung cancer.Curr Probl Cancer. 2024 Feb;48:101035. doi: 10.1016/j.currproblcancer.2023.101035. Epub 2023 Nov 20. Curr Probl Cancer. 2024. PMID: 37988903
-
Cancer, Phase Angle and Sarcopenia: The Role of Diet in Connection with Lung Cancer Prognosis.Lung. 2022 Jun;200(3):347-379. doi: 10.1007/s00408-022-00536-z. Epub 2022 May 26. Lung. 2022. PMID: 35616720 Review.
-
Eicosapentaenoic acid in cancer improves body composition and modulates metabolism.Nutrition. 2015 Apr;31(4):549-55. doi: 10.1016/j.nut.2014.12.002. Epub 2014 Dec 12. Nutrition. 2015. PMID: 25770317 Review.
References
-
- Li ZH, Ji S, Hu XW, Chen X, Liu H, Sun Y, et al. . Analysis of risk factors of sarcopenia in patients with lung cancer and its correlation with clinical prognosis. Chin J Gen Med. (2021) 24:3310–5+3322. doi: 10.12114/j.issn.1007-9572.2021.00.599 - DOI
-
- Liang KC, Hidenori A, Prasert A, Wang J, Chen LK, Assantachai P, et al. . Roles of nutrition in muscle health of community-dwelling older adults: Evidence-based expert consensus from Asian Working Group for Sarcopenia. J Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle. (2022) 13:1653–72. doi: 10.1002/jcsm.12981 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources