Relationship between muscle quality index and urinary incontinence among U.S. population: evidence from NHANES 2011 to 2014
- PMID: 40265166
- PMCID: PMC12011557
- DOI: 10.3389/fendo.2025.1533617
Relationship between muscle quality index and urinary incontinence among U.S. population: evidence from NHANES 2011 to 2014
Abstract
Background: Urinary incontinence (UI) is a common and troublesome global problem. The purpose was to explore the relationship between muscle quality index (MQI) and UI.
Methods: We performed a secondary analysis of the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) database (2011 to 2014). Weighted logistic regression was used to analyze the relationship between MQI and UI. Subgroup analyses were further conducted to investigate the relationship. The P for trend and P for interaction were also conducted.
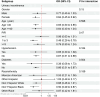
Results: A total of 2,779 participants were enrolled in the study, comprising 1,241 females and 1,538 males with a median age of 36 years. The prevalence of UI was approximately 25.45%. In adjusted model, weighted multivariate logistic regression analyses showed that MQI was significantly negatively associated with UI (OR,0.65; 95%CI,0.50 to 0.85). Furthermore, the results revealed that the highest MQI group had a 33% reduction in UI compared to the lowest MQI group and the P for trend was less than 0.05. In subgroup analysis, the MQI was negatively associated with UI in females (OR, 0.64; 95%CI, 0.45 to 0.92), under 40 years old (OR,0.65; 95%CI,0.50 to 0.85), poverty-to-income ratio of 1 to 3 (OR, 0.48; 95%CI, 0.29 to 0.78), and Non-Hispanic Black (OR, 0.50; 95%CI, 0.29 to 0.87), and in some populations without hypertension or diabetes.
Conclusion: The study revealed that a higher MQI was associated with a lower prevalence of urinary incontinence. This study provides insights into potential preventive strategies for UI.
Keywords: NHANES; cohort study; epidemiology; muscle quality index; urinary incontinence.
Copyright © 2025 Hu, Xu, Xie, Chen and Lei.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Association between triglyceride glucose body mass index and urinary incontinence: a cross-sectional study from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) 2001 to 2018.Lipids Health Dis. 2024 Sep 20;23(1):304. doi: 10.1186/s12944-024-02306-7. Lipids Health Dis. 2024. PMID: 39304881 Free PMC article.
-
The association between non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and urinary incontinence among adult females in the United States.BMC Public Health. 2024 May 22;24(1):1373. doi: 10.1186/s12889-024-18578-8. BMC Public Health. 2024. PMID: 38778285 Free PMC article.
-
Weight-adjusted-waist index is positively associated with urinary incontinence: results from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) 2001-2018.Eur J Med Res. 2024 Jul 16;29(1):368. doi: 10.1186/s40001-024-01971-9. Eur J Med Res. 2024. PMID: 39014459 Free PMC article.
-
Associations between metabolic score for visceral fat and urinary incontinence among US adult women: a population-based cross-sectional study.BMC Public Health. 2025 Mar 9;25(1):932. doi: 10.1186/s12889-025-21966-3. BMC Public Health. 2025. PMID: 40059144 Free PMC article.
-
Pelvic floor muscle training for preventing and treating urinary and faecal incontinence in antenatal and postnatal women.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 May 6;5(5):CD007471. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD007471.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020. PMID: 32378735 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Li J, Xie R, Tian H, Wang D, Mo M, Yang J, et al. . Association between triglyceride glucose body mass index and urinary Incontinence: A cross-sectional study from the national health and nutrition examination survey (Nhanes) 2001 to 2018. Lipids Health Dis. (2024) 23:304. doi: 10.1186/s12944-024-02306-7 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical