Efficacy and safety of compound glycyrrhizin in patients with alopecia areata: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 40265259
- PMCID: PMC12020145
- DOI: 10.1080/07853890.2025.2491659
Efficacy and safety of compound glycyrrhizin in patients with alopecia areata: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
Background: Although compound glycyrrhizin (CG) has been widely used to alopecia areata (AA) in China, its efficacy and safety remain unclear. This systematic review and meta-analysis aimed to evaluate the efficacy and safety of CG for AA.
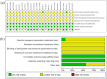
Materials and methods: Eight literature databases were retrieved from their inceptions to 29 February 2024 to identify the eligible randomized controlled trials comparing CG plus conventional treatments with conventional treatments alone for the treatment of AA. Risk ratio (RR), mean difference and 95% confidence interval (CI) were used to estimate the pooled results. RevMan 5.4 (Cochrane Collaboration, Copenhagen, Denmark) and Stata 12.0 software (StataCorp., College Station, TX) were used for statistical analysis.
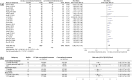
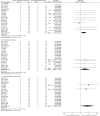
Results: A total of 23 eligible studies with 2219 patients were included. The pooled results revealed that CG plus conventional treatments was superior to conventional treatments alone in cure rate (RR = 1.60, 95%CI [1.47, 1.74], p < .001), total efficacy rate (RR = 1.37, 95%CI [1.29, 1.45], p < .001) and the Severity of Alopecia Tool (SALT) score, regardless of different conventional treatments, treatment courses and doses of CG. In terms of safety, a few patients suffered from adverse events (AEs), including oedema, elevated blood pressure and gastrointestinal tract discomfort, and the incidence of oedema was higher in the patients receiving CG (RR = 2.53, 95%CI [1.04, 6.19], p = .04).
Conclusions: The combination of CG and conventional treatments was effective and safe for patients with AA, and CG could promote hair regrowth with mild AEs.
Keywords: Adverse reactions; alopecia areata; compound glycyrrhizin; effectiveness; meta-analysis.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest was reported by the author(s).
Figures


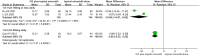

Similar articles
-
Efficacy and safety of compound glycyrrhizin combined with topical minoxidil for alopecia areata: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials.J Dermatolog Treat. 2024 Dec;35(1):2381766. doi: 10.1080/09546634.2024.2381766. Epub 2024 Sep 4. J Dermatolog Treat. 2024. PMID: 39230160
-
Efficacy and safety of compound glycyrrhizin in the patients with vitiligo: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Expert Rev Clin Pharmacol. 2023 Jan-Jun;16(6):601-611. doi: 10.1080/17512433.2023.2213887. Epub 2023 May 23. Expert Rev Clin Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 37218470
-
Efficacy and safety of compound glycyrrhizin in combination with conventional therapy in treatment of vitiligo: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials.Medicine (Baltimore). 2023 Oct 27;102(43):e35533. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000035533. Medicine (Baltimore). 2023. PMID: 37904437 Free PMC article.
-
A randomized controlled trial comparing total glucosides of paeony capsule and compound glycyrrhizin tablet for alopecia areata.Chin J Integr Med. 2012 Aug;18(8):621-5. doi: 10.1007/s11655-012-1173-0. Epub 2012 Aug 2. Chin J Integr Med. 2012. PMID: 22855038 Clinical Trial.
-
Compound glycyrrhizin combined with antihistamines for chronic urticaria: A protocol for systematic review and meta analysis.Medicine (Baltimore). 2020 Aug 14;99(33):e21624. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000021624. Medicine (Baltimore). 2020. PMID: 32872021 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
