The Influence of Financial Incentives on Vaccination Hesitancy: A Narrative Review of Recent Research
- PMID: 40266112
- PMCID: PMC11946546
- DOI: 10.3390/vaccines13030256
The Influence of Financial Incentives on Vaccination Hesitancy: A Narrative Review of Recent Research
Abstract
Background: Vaccine hesitancy represents a significant global health challenge that greatly hinders public health efforts focused on managing the transmission of infectious diseases. A wealth of original research conducted worldwide has examined various incentives that could help alleviate vaccine hesitancy and increase vaccination rates. Although some findings are conflicting, no comprehensive review has yet assessed the overall effectiveness of these strategies. This study aims to bridge this knowledge gap by examining how financial incentives influence people's willingness to undergo vaccination.
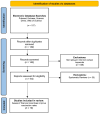
Methods: In August 2024, we extensively searched four databases for studies focusing on financial incentives and vaccination rates. Examples of financial incentives included lottery tickets and hypothetical or physical monetary rewards ranging in various amounts depending on the study. We selected nineteen relevant articles from a larger pool and evaluated them for validity and bias.
Results: Around eighty percent of the research focused on COVID-19 vaccines, driven by the ongoing pandemic and the debates surrounding their use. Most of the studies indicated a positive influence of financial incentives on vaccination rates, although they often came with a higher risk of bias. Conversely, several studies suggest that financial incentives do not result in benefits. Instead, they highlight other factors that have a more profound effect on influencing people to undergo vaccination. The remaining studies are inconclusive regarding the effectiveness of financial incentives, concluding the need for further research. The strategies to mitigate these concerns included a combination of legal and monetary incentives.
Summary: The effectiveness of financial incentives in boosting vaccination rates seems to differ significantly based on the region and context. They tend to be more effective in economically disadvantaged developing countries. In contrast, in developed nations, they may be ineffective or counterproductive due to various confounding factors such as financial background, lack of trust in the healthcare system, and/or lack of patient education. In resource-rich areas, educational programs often yield better results, and addressing widespread mistrust in healthcare systems and governmental policies through transparency is essential. Ultimately, employing tailored incentives alongside public education could enhance vaccination acceptance, particularly in culturally diverse countries like the United States, where understanding community preferences is crucial.
Keywords: financial; hesitancy; incentive; monetary; vaccine.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Impact of summer programmes on the outcomes of disadvantaged or 'at risk' young people: A systematic review.Campbell Syst Rev. 2024 Jun 13;20(2):e1406. doi: 10.1002/cl2.1406. eCollection 2024 Jun. Campbell Syst Rev. 2024. PMID: 38873396 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Improving vaccination uptake among adolescents.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Jan 17;1(1):CD011895. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011895.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020. PMID: 31978259 Free PMC article.
-
Providing freedom or financial remuneration? A cross-sectional study on the role of monetary and legal incentives on COVID-19 further booster vaccination intention in the Italian context.Front Public Health. 2023 Jun 20;11:1186429. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2023.1186429. eCollection 2023. Front Public Health. 2023. PMID: 37408739 Free PMC article.
-
Addressing vaccine hesitancy and resistance for COVID-19 vaccines.Int J Nurs Stud. 2022 Jul;131:104241. doi: 10.1016/j.ijnurstu.2022.104241. Epub 2022 Apr 1. Int J Nurs Stud. 2022. PMID: 35489108 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A rapid review of evidence on the determinants of and strategies for COVID-19 vaccine acceptance in low- and middle-income countries.J Glob Health. 2021 Nov 20;11:05027. doi: 10.7189/jogh.11.05027. eCollection 2021. J Glob Health. 2021. PMID: 34912550 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Pandemic paradox: How the COVID-19 crisis transformed vaccine hesitancy into a two-edged sword.Hum Vaccin Immunother. 2025 Dec;21(1):2543167. doi: 10.1080/21645515.2025.2543167. Epub 2025 Aug 12. Hum Vaccin Immunother. 2025. PMID: 40791124 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Spees L.P., Biddell C.B., Angove R.S.M., Gallagher K.D., Anderson E., Christenbury A., Rocque G., Wheeler S.B. Barriers to COVID-19 vaccine uptake among resource-limited adults diagnosed with chronic illness. Front. Public Health. 2023;11:1046515. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2023.1046515. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous