Evaluating the Immunogenicity, Efficacy, and Effectiveness of Recombinant Zoster Vaccine for Global Public Health Policy
- PMID: 40266145
- PMCID: PMC11946835
- DOI: 10.3390/vaccines13030250
Evaluating the Immunogenicity, Efficacy, and Effectiveness of Recombinant Zoster Vaccine for Global Public Health Policy
Abstract
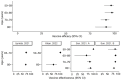
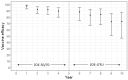
Background: Herpes zoster (HZ) is a painful neurocutaneous disease caused by the varicella-zoster virus. The recombinant zoster vaccine (RZV) is becoming increasingly incorporated into national vaccination schedules. We aimed to evaluate RZV from a global public health policy perspective. Methods: We performed a rapid review of studies evaluating the immunogenicity, efficacy, and effectiveness of RZV for protection against HZ and associated complications. We searched PubMed for English-language studies published between 7 August 2012 and 30 September 2023. Included studies reported vaccine efficacy or effectiveness against HZ and HZ-associated complications. Immunogenicity studies were included if they contributed to the understanding of RZV protection over time and/or co-administration with other vaccines. HZ outcomes were stratified by socio-demographic and clinical variables. Results: From 405 identified publications, 33 were eligible for the study. Most studies were conducted in the US (N = 12), across North America (N = 10), and Europe (N = 5), or across multiple locations across North America, Latin America, and Asia-Australia (N = 6). Vaccine efficacy against HZ in immunocompetent populations ranged between 90% and 97%, while effectiveness ranged between 71% and 86%. Protection stayed above 70% for at least 10 years, with no significant differences by age or ethnicity. Conclusions: RZV is effective in reducing the risk of HZ and its associated complications. Protection is long-lasting and the vaccine is suitable for older and immunocompromised populations. However, the decision to incorporate the vaccine into national policies depends on additional factors (e.g., cost-effectiveness), which may be difficult to characterize without an understanding of the global disease burden.
Keywords: health policy; herpes zoster; immunization; vaccine; varicella zoster virus.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Recombinant zoster vaccine in immunocompetent and immunocompromised adults: A review of clinical studies.Hum Vaccin Immunother. 2023 Dec 15;19(3):2278362. doi: 10.1080/21645515.2023.2278362. Epub 2023 Nov 15. Hum Vaccin Immunother. 2023. PMID: 37965770 Free PMC article. Review.
-
How large could the public health impact of introducing recombinant zoster vaccination for people aged ≥50 years in five Latin American countries be?Hum Vaccin Immunother. 2023 Dec 31;19(1):2164144. doi: 10.1080/21645515.2022.2164144. Epub 2023 Feb 23. Hum Vaccin Immunother. 2023. PMID: 36821856 Free PMC article.
-
A practitioner's guide to the recombinant zoster vaccine: review of national vaccination recommendations.Expert Rev Vaccines. 2021 Sep;20(9):1065-1075. doi: 10.1080/14760584.2021.1956906. Epub 2021 Sep 1. Expert Rev Vaccines. 2021. PMID: 34311643 Review.
-
Cost-effectiveness of the recombinant zoster vaccine (RZV) against herpes zoster: An updated critical review.Hum Vaccin Immunother. 2023 Dec 31;19(1):2168952. doi: 10.1080/21645515.2023.2168952. Epub 2023 Mar 14. Hum Vaccin Immunother. 2023. PMID: 36916240 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Summary of the NACI Update on Herpes Zoster Vaccines.Can Commun Dis Rep. 2018 Sep 6;44(9):220-225. doi: 10.14745/ccdr.v44i09a06. eCollection 2018 Sep 6. Can Commun Dis Rep. 2018. PMID: 31015813 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Harpaz R., Ortega-Sanchez I.R., Seward J.F. Prevention of herpes zoster: Recommendations of the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices (ACIP) MMWR Recomm. Rep. 2008;57:1–30; quiz CE2–CE4. - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

