Exploring CD169+ Macrophages as Key Targets for Vaccination and Therapeutic Interventions
- PMID: 40266235
- PMCID: PMC11946325
- DOI: 10.3390/vaccines13030330
Exploring CD169+ Macrophages as Key Targets for Vaccination and Therapeutic Interventions
Abstract
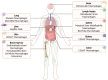
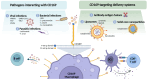
CD169 is a sialic acid-binding immunoglobulin-like lectin (Siglec-1, sialoadhesin) that is expressed by subsets of tissue-resident macrophages and circulating monocytes. This receptor interacts with α2,3-linked Neu5Ac on glycoproteins as well as glycolipids present on the surface of immune cells and pathogens. CD169-expressing macrophages exert tissue-specific homeostatic functions, but they also have opposing effects on the immune response. CD169+ macrophages act as a pathogen filter, protect against infectious diseases, and enhance adaptive immunity, but at the same time pathogens also exploit them to enable further dissemination. In cancer, CD169+ macrophages in tumor-draining lymph nodes are correlated with better clinical outcomes. In inflammatory diseases, CD169 expression is upregulated on monocytes and on monocyte-derived macrophages and this correlates with the disease state. Given their role in promoting adaptive immunity, CD169+ macrophages are currently investigated as targets for vaccination strategies against cancer. In this review, we describe the studies investigating the importance of CD169 and CD169+ macrophages in several disease settings and the vaccination strategies currently under investigation.
Keywords: CD169; Siglec-1; adaptive immunity; antigen-presenting cells; dendritic cells; macrophages; sialoadhesin; therapeutic interventions; vaccines.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Targeted delivery of lipid antigen to macrophages via the CD169/sialoadhesin endocytic pathway induces robust invariant natural killer T cell activation.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2013 May 7;110(19):7826-31. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1219888110. Epub 2013 Apr 22. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2013. PMID: 23610394 Free PMC article.
-
CD169+ Macrophages Capture and Dendritic Cells Instruct: The Interplay of the Gatekeeper and the General of the Immune System.Front Immunol. 2018 Oct 26;9:2472. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.02472. eCollection 2018. Front Immunol. 2018. PMID: 30416504 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Comparison of Protein and Peptide Targeting for the Development of a CD169-Based Vaccination Strategy Against Melanoma.Front Immunol. 2018 Sep 6;9:1997. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.01997. eCollection 2018. Front Immunol. 2018. PMID: 30237798 Free PMC article.
-
Research progress on CD169-positive macrophages in tumors.Am J Transl Res. 2021 Aug 15;13(8):8589-8597. eCollection 2021. Am J Transl Res. 2021. PMID: 34539981 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Selective tumor antigen vaccine delivery to human CD169+ antigen-presenting cells using ganglioside-liposomes.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2020 Nov 3;117(44):27528-27539. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2006186117. Epub 2020 Oct 16. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2020. PMID: 33067394 Free PMC article.
References
-
- York M.R., Nagai T., Mangini A.J., Lemaire R., van Seventer J.M., Lafyatis R. A macrophage marker, Siglec-1, is increased on circulating monocytes in patients with systemic sclerosis and induced by type I interferons and toll-like receptor agonists. Arthritis Rheum. 2007;56:1010–1020. doi: 10.1002/art.22382. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources