ApoM-bound S1P acts via endothelial S1PR1 to suppress choroidal neovascularization and vascular leakage
- PMID: 40266369
- PMCID: PMC12018641
- DOI: 10.1007/s10456-025-09975-7
ApoM-bound S1P acts via endothelial S1PR1 to suppress choroidal neovascularization and vascular leakage
Abstract
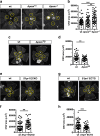
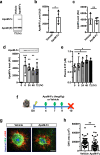
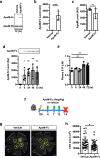
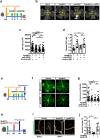
Neovascular age-related macular degeneration (nAMD) is a major cause of vision loss worldwide. Current standard of care is repetitive intraocular injections of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) inhibitors, although responses may be partial and non-durable. We report that circulating sphingosine 1-phosphate (S1P) carried by apolipoprotein M (ApoM) acts through the endothelial S1P receptor 1 (S1PR1) to suppress choroidal neovascularization (CNV) in mouse laser-induced CNV, modeling nAMD. In humans, low plasma ApoM levels were associated with increased choroidal and retinal pathology. Additionally, endothelial S1pr1 knockout and overexpressing transgenic mice showed increased and reduced CNV lesion size, respectively. Systemic administration of ApoM-Fc, an engineered S1P chaperone protein, not only attenuated CNV to an equivalent degree as anti-VEGF antibody treatment but also suppressed pathological vascular leakage. We suggest that modulating circulating ApoM-bound S1P action on endothelial S1PR1 provides a novel therapeutic strategy to treat nAMD.
Keywords: Age-related macular degeneration; Angiogenesis; Apolipoprotein M; High-density lipoprotein; Sphingosine 1-phosphate; Vascular leak.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Conflict of interest: TH and LEHS are listed as inventors on patent applications on ApoM-Fc. TH and AJD are founders of Apovita Therapeutics, Inc.
Figures
References
-
- Mitchell P, Liew G, Gopinath B, Wong TY (2018) Age-related macular degeneration. Lancet 392(10153):1147–1159 - PubMed
-
- Guillonneau X, Eandi CM, Paques M, Sahel JA, Sapieha P, Sennlaub F (2017) On phagocytes and macular degeneration. Prog Retin Eye Res 61:98–128 - PubMed
-
- Fleckenstein M, Keenan TDL, Guymer RH, Chakravarthy U, Schmitz-Valckenberg S, Klaver CC et al (2021) Age-related macular degeneration. Nat Rev Dis Primers 7(1):31 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

