Content Validity and Psychometric Validation of an Adapted Version of the Subject Sleep Diary in Prurigo Nodularis
- PMID: 40266487
- PMCID: PMC12092868
- DOI: 10.1007/s13555-025-01406-1
Content Validity and Psychometric Validation of an Adapted Version of the Subject Sleep Diary in Prurigo Nodularis
Abstract
Introduction: Patients with prurigo nodularis (PN) often experience sleep disturbance. A psychometric evaluation was conducted to assess the suitability of a PN-adapted multi-item subject sleep diary (SSD) for measuring PN-related sleep disturbance.
Methods: Content validity of the SSD was evaluated through qualitative interviews with adults with PN (N = 21). Psychometric properties of SSD parameters (sleep onset latency [SOL], wakefulness after sleep onset [WASO], total awake time [TWT], total sleep time [TST], sleep efficiency [SE], PN-related WASO [WASO-PN], number of WASO-PN, and sleep quality/refresh [SQR]) were evaluated using data from adults with moderate-to-severe PN in the phase 3 OLYMPIA trials (NCT04501666 [N = 286], NCT04501679 [N = 274]). The relationship between SSD parameters and the single-item Sleep Disturbance Numerical Rating Scale (SD-NRS) was examined using equipercentile linking.
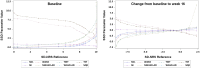
Results: Most interview participants who responded to cognitive debriefing questions understood the SSD as intended (≥ 80% for each item), confirming content validity. All SSD parameters showed good test-retest reliability. At week 16, all SSD parameters but TST showed moderate-to-strong correlations, in the expected direction, with the SD-NRS, Peak Pruritus NRS (PP-NRS), Average Pruritus (AP) NRS, Dermatology Life Quality Index (DLQI), PN-related pain frequency and intensity, Prurigo Activity and Severity Score (PAS), and/or Investigator's Global Assessment (IGA). Known-groups validity was adequate for all SSD parameters based on the Patient Global Impression of Severity-Sleep Disturbance (PGIS-SD), Patient Global Assessment of Disease (PGAD), PP-NRS, DLQI, and/or IGA. All parameters but TST were responsive to improvements on the PGIS-SD, Patient Global Impression of Change-Sleep Disturbance, PGAD, PP-NRS, AP NRS, PN-related pain intensity, DLQI, and/or IGA. Cross-sectional values or value changes of the SD-NRS were moderately to strongly correlated with SSD parameters, and equipercentile linking analyses revealed non-linear relationships between the measures.
Conclusions: The findings suggest that the SSD is a fit-for-purpose measure that can be used to assess sleep disturbance in moderate-to-severe PN.
Clinical trial registration: NCT04501666, NCT04501679.
Keywords: Patient-reported outcome; Prurigo nodularis; Psychometrics; Sleep diary; Sleep disturbance.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Conflict of Interest: Sonja Ständer has been a speaker, consultant, investigator, and/or recipient of research funding from Abbvie, Almirall, Beiersdorf, BMS, Clexio, Eli Lilly, FomF, Galderma, Integrity CE, Kiniksa, Leo Pharma, L’Oréal, MEDahead, Moroscience, NACCME, Novartis, Omnicuris, P.G. Unna Academy, Pfizer, Sanofi, TouchIME, UCB, Vifor, and WebMD. Shawn G. Kwatra is an advisory board member/consultant for Abbvie, Aslan Pharmaceuticals, Arcutis Biotherapeutics, Castle Biosciences, Celldex Therapeutics, Galderma, Genzada Pharmaceuticals, Incyte Corporation, Johnson & Johnson, Leo Pharma, Novartis Pharmaceuticals Corporation, Pfizer, Regeneron Pharmaceuticals, and Sanofi and has served as an investigator for Galderma, Incyte, Pfizer, and Sanofi. Dr. Kwatra’s current affiliation is Maryland Itch Center, University of Maryland School of Medicine, Baltimore, MD, USA. Danielle N. Rodriguez, Carla Dias-Barbosa, and Dina Filipenko are employees of Evidera, which was paid by Galderma for work relating to this study. Christophe Piketty, Zarif Jabbar-Lopez, and Jorge Puelles are employees of Galderma, which funded this study. Henning Wiegmann have no conflicts of interest to declare. Ethical Approval: Ethics approval for the qualitative interview study was obtained from Advarra (Columbia, MD; reference number Pro00044847), and participants provided written informed consent before taking part. The OLYMPIA trials were conducted in accordance with the Helsinki Declaration of 1964 and its later amendments, good clinical practice guidelines, and International Council for Harmonisation of Technical Requirements for Pharmaceuticals for Human Use guidelines. Both trials received ethical approval from applicable regulatory authorities and the independent ethics committee or institutional review board at each participating site before study initiation. All participants provided written informed consent.
Figures
References
-
- Stander HF, Elmariah S, Zeidler C, Spellman M, Ständer S. Diagnostic and treatment algorithm for chronic nodular prurigo. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2020;82(2):460–8. - PubMed
-
- Huang AH, Canner JK, Khanna R, Kang S, Kwatra SG. Real-world prevalence of prurigo nodularis and burden of associated diseases. J Invest Dermatol. 2020;140(2):480-483.e484. - PubMed
-
- Steinke S, Zeidler C, Riepe C, et al. Humanistic burden of chronic pruritus in patients with inflammatory dermatoses: results of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology Network on Assessment of Severity and Burden of Pruritus (PruNet) cross-sectional trial. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2018;79(3):457-463.e455. - PubMed
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

