Tauroursodeoxycholic Acid Enhances the Quality of Postovulatory Aged Oocytes by Alleviating Oxidative Stress, Apoptosis, and Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress in Pigs
- PMID: 40266976
- PMCID: PMC11946076
- DOI: 10.3390/vetsci12030265
Tauroursodeoxycholic Acid Enhances the Quality of Postovulatory Aged Oocytes by Alleviating Oxidative Stress, Apoptosis, and Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress in Pigs
Abstract
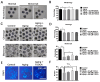
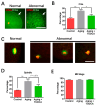
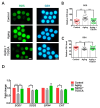
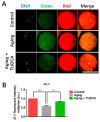
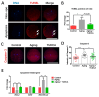
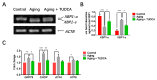
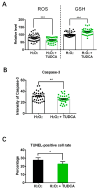
One of the major factors causing reduced developmental capacity of aged porcine oocytes is the induction of oxidative stress during oocyte aging. Tauroursodeoxycholic acid (TUDCA) supports cellular function by acting as an antioxidant and free radical scavenger. The aim of this study is to evaluate whether exogenous supplementation of TUDCA to the porcine in vitro maturation system can ameliorate the compromised quality of aged oocytes by mitigating free radical production. We found that TUDCA was able to effectively maintain normal oocyte morphology, cortical granule distribution, and spindle structure during postovulatory aging. Additionally, the blastocyst rate and total cell number in blastocysts were significantly increased in aged porcine oocytes treated with TUDCA. Importantly, aged porcine oocytes treated with TUDCA reduced ROS levels, increased the expression levels of GSH and SOD1 genes, and improved the mitochondrial membrane potential ratio. Further study demonstrated that TUDCA significantly alleviated apoptosis in aged porcine oocytes, confirmed by the decreased Caspase 3 levels and ratio of BAX to BCL2. Interestingly, TUDCA could effectively alleviate the phenomenon of endoplasmic reticulum stress triggered during the oocyte aging process. Taking these findings together, our study demonstrates that TUDCA supplementation beneficially affects the quality of aged porcine oocytes by suppressing oxidative stress, apoptosis, and endoplasmic reticulum stress.
Keywords: ROS; apoptosis; endoplasmic reticulum stress; postovulatory aged oocyte; tauroursodeoxycholic acid.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Cadmium exposure impairs oocyte meiotic maturation by inducing endoplasmic reticulum stress in vitro maturation of porcine oocytes.Toxicol In Vitro. 2023 Sep;91:105615. doi: 10.1016/j.tiv.2023.105615. Epub 2023 May 18. Toxicol In Vitro. 2023. PMID: 37207789
-
Tauroursodeoxycholic acid improves pre-implantation development of porcine SCNT embryo by endoplasmic reticulum stress inhibition.Reprod Biol. 2016 Dec;16(4):269-278. doi: 10.1016/j.repbio.2016.10.003. Epub 2016 Oct 17. Reprod Biol. 2016. PMID: 27765486
-
Attenuation of endoplasmic reticulum stress improves invitro growth and subsequent maturation of bovine oocytes.Theriogenology. 2024 Oct 15;228:54-63. doi: 10.1016/j.theriogenology.2024.07.027. Epub 2024 Jul 31. Theriogenology. 2024. PMID: 39096624
-
Treatment of in vitro-Matured Bovine Oocytes With Tauroursodeoxycholic Acid Modulates the Oxidative Stress Signaling Pathway.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021 Feb 19;9:623852. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2021.623852. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021. PMID: 33681203 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular mechanism of poor embryo development in postovulatory aged oocytes: mini review.J Obstet Gynaecol Res. 2013 Oct;39(10):1431-9. doi: 10.1111/jog.12111. Epub 2013 Jul 22. J Obstet Gynaecol Res. 2013. PMID: 23876057 Review.
References
-
- Xing X., Zhang J., Zhang J., Wang Y., Wang J., Kang J., Quan F., Su J., Zhang Y. Coenzyme Q10 Supplement Rescues Postovulatory Oocyte Aging by Regulating SIRT4 Expression. Curr. Mol. Pharmacol. 2022;15:190–203. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

