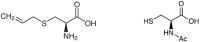Evaluation of intake of aged garlic extract and organosulfur compounds on progressive hearing loss in DBA/2J mice
- PMID: 40267072
- PMCID: PMC12017496
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0322105
Evaluation of intake of aged garlic extract and organosulfur compounds on progressive hearing loss in DBA/2J mice
Abstract
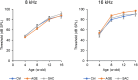
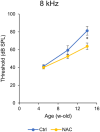
Garlic is rich in organosulfur compounds with high antioxidant capacity and is known to have various health benefits. Aged garlic is a particularly effective source of these active compounds because it contains fewer toxic components. This study evaluated the effects of S-allyl cysteine (SAC), a major functional organosulfur compound in garlic, and aged garlic extract (AGE) on the suppression of progressive hearing loss. SAC and AGE were dissolved in drinking water at 1% (w/w) and administered to DBA/2J mice, a model of early progressive hearing loss, for 12 weeks, starting at 4 weeks of age. While the results revealed a trend toward weight loss in the SAC group, the weight of the AGE group was comparable to that of the control group, and no adverse events were observed in either group. The hearing ability of the mice was measured using auditory brainstem responses at 4, 8, 12, and 16 weeks of age. Hearing loss at 8 and 16 kHz progressed over the 12-week period, with neither sample inhibiting hearing loss. In contrast, another organosulfur compound, N-acetylcysteine (NAC), administered in 1% w/w drinking water and evaluated for hearing loss over time, significantly suppressed hearing loss progression in DBA/2J mice. These results indicate that the NAC and SAC differ in their ability to prevent hearing loss and demonstrate that the inhibitory effects of functional food components on hearing loss can be evaluated over a short period in DBA/2J mice.
Copyright: © 2025 Oike et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Conflict of interest statement
I have read the journal's policy and the authors of this manuscript have the following competing interests: [Momoya Co. Ltd. manufactures and sells AGE].
Figures
Similar articles
-
Otoprotective effects of mouse nerve growth factor in DBA/2J mice with early-onset progressive hearing loss.J Neurosci Res. 2017 Oct;95(10):1937-1950. doi: 10.1002/jnr.24056. Epub 2017 Mar 27. J Neurosci Res. 2017. PMID: 28345280 Free PMC article.
-
Nonenzymatic antioxidant activity of four organosulfur compounds derived from garlic.J Agric Food Chem. 2002 Oct 9;50(21):6143-7. doi: 10.1021/jf0204203. J Agric Food Chem. 2002. PMID: 12358493
-
Cholesterol-lowering effect of garlic extracts and organosulfur compounds: human and animal studies.J Nutr. 2001 Mar;131(3s):989S-93S. doi: 10.1093/jn/131.3.989S. J Nutr. 2001. PMID: 11238803 Review.
-
Which Constituents Determine the Antioxidant Activity and Cytotoxicity of Garlic? Role of Organosulfur Compounds and Phenolics.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Aug 1;25(15):8391. doi: 10.3390/ijms25158391. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39125961 Free PMC article.
-
Therapeutic Potential of Stable Organosulfur Compounds of Aged Garlic.Cardiovasc Hematol Agents Med Chem. 2023;21(2):84-95. doi: 10.2174/1871525721666221020123056. Cardiovasc Hematol Agents Med Chem. 2023. PMID: 36278448 Review.
References
-
- WHO. World report on hearing. World Health Organization; 2021.
-
- WD W, H A, RJH S. Hereditary hearing loss homepage.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources