Acute BRCAness induction and AR pathway blockage through CDK12/7/9 degradation enhances PARP inhibitor sensitivity in prostate cancer
- PMID: 40267193
- PMCID: PMC12017310
- DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.adu0847
Acute BRCAness induction and AR pathway blockage through CDK12/7/9 degradation enhances PARP inhibitor sensitivity in prostate cancer
Abstract
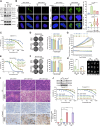
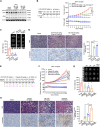
Current treatments for advanced prostate cancer (PCa) primarily target the androgen receptor (AR) pathway. However, the emergence of castration-resistant prostate cancer (CRPC) and resistance to AR pathway inhibitors (APPIs) remains ongoing challenges. Here, we present BSJ-5-63, a proteolysis-targeting chimera (PROTAC) targeting cyclin-dependent kinases (CDKs) CDK12, CDK7, and CDK9, offering a multipronged approach to CRPC therapy. BSJ-5-63 degrades CDK12, diminishing BRCA1 and BRCA2 expression and inducing a sustained "BRCAness" state. This sensitizes cancer cells to PARP inhibitors (PARPis) regardless of their homologous recombination repair (HRR) status. Furthermore, CDK7 and CDK9 degradation attenuates AR signaling, enhancing its therapeutic efficacy. Preclinical studies, including both in vitro and in vivo CRPC models, demonstrate that BSJ-5-63 exerts potent antitumor activity in both AR-positive and AR-negative setting. This study introduces BSJ-5-63 as a promising therapeutic agent that addresses both DNA repair and AR signaling mechanisms, with potential benefits for a board patient population.
Figures





Update of
-
Acute BRCAness Induction and AR Signaling Blockage through CDK12/7/9 Degradation Enhances PARP Inhibitor Sensitivity in Prostate Cancer.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Nov 7:2024.07.09.602803. doi: 10.1101/2024.07.09.602803. bioRxiv. 2024. Update in: Sci Adv. 2025 Apr 25;11(17):eadu0847. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.adu0847. PMID: 39026842 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
References
-
- Siegel R. L., Giaquinto A. N., Jemal A., Cancer statistics, 2024. CA Cancer J. Clin. 74, 12–49 (2024). - PubMed
-
- E. Lee, Z. Zhang, C. C. Chen, D. Choi, A. C. A. Rivera, E. Linton, Y. J. Ho, J. Love, J. LaClair, J. Wongvipat, C. L. Sawyers, Timing of treatment shapes the path to androgen receptor signaling inhibitor resistance in prostate cancer. bioRxiv 585532 [Preprint] (2024). 10.1101/2024.03.18.585532. - DOI
-
- Abida W., Cyrta J., Heller G., Prandi D., Armenia J., Coleman I., Cieslik M., Benelli M., Robinson D., Van Allen E. M., Sboner A., Fedrizzi T., Mosquera J. M., Robinson B. D., De Sarkar N., Kunju L. P., Tomlins S., Wu Y. M., Nava Rodrigues D., Loda M., Gopalan A., Reuter V. E., Pritchard C. C., Mateo J., Bianchini D., Miranda S., Carreira S., Rescigno P., Filipenko J., Vinson J., Montgomery R. B., Beltran H., Heath E. I., Scher H. I., Kantoff P. W., Taplin M. E., Schultz N., deBono J. S., Demichelis F., Nelson P. S., Rubin M. A., Chinnaiyan A. M., Sawyers C. L., Genomic correlates of clinical outcome in advanced prostate cancer. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 116, 11428–11436 (2019). - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

