A new method to measure cell metabolism of rare cells in vivo reveals a high oxidative phosphorylation dependence of lung T cells
- PMID: 40268295
- PMCID: PMC12392706
- DOI: 10.1111/imcb.70018
A new method to measure cell metabolism of rare cells in vivo reveals a high oxidative phosphorylation dependence of lung T cells
Abstract
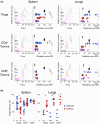
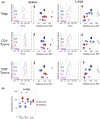
Regulation of cellular metabolism is a central element governing the fate and function of T cells. However, the in vivo metabolic characteristics of rare cells, such as nonlymphoid tissue T cells, are poorly understood because of experimental limitations. Most techniques measuring cell metabolism require large cell numbers. The recent SCENITH method allows for studying the metabolism of rare cells by flow cytometry. However, this technique requires cells to be isolated and cultured ex vivo, which may alter their metabolism. Here, we propose a new experimental approach, called in vivo SCENITH, to investigate the cellular metabolism of T cells in vivo at a steady state in the spleen and lungs. For this purpose, we administered the metabolic modulators directly in mice, instead of applying these reagents ex vivo, as in the classical SCENITH method. Whereas ex vivo manipulation impacted the viability and phenotype of T cells, this toxic effect was not observed in the in vivo SCENITH. We observed that conventional and regulatory T cells shared similar metabolic profiles. Importantly, whereas spleen T cells used both oxidative phosphorylation and glycolysis, the metabolism of T cells in the lungs was mainly based on oxidative phosphorylation. Finally, metabolic inhibitors that interfere with protein translation and energy availability downregulated Foxp3 expression in regulatory T cells. These results describe an expansion of SCENITH that allows to measure the metabolic profile of rare cells in vivo, revealing a high dependence on oxidative phosphorylation of lung T cells.
Keywords: Cell metabolism; Foxp3; Treg; in vivo SCENITH; lung T cells.
© 2025 The Author(s). Immunology & Cell Biology published by John Wiley & Sons Australia, Ltd on behalf of the Australian and New Zealand Society for Immunology, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors do not have any conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Prescription of Controlled Substances: Benefits and Risks.2025 Jul 6. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. 2025 Jul 6. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. PMID: 30726003 Free Books & Documents.
-
Method to Study Metabolism in Lymphoid Cells using Chemistry to Measure Puromycin Incorporation by Flow Cytometry.J Vis Exp. 2025 Aug 15;(222). doi: 10.3791/67377. J Vis Exp. 2025. PMID: 40889248
-
The Black Book of Psychotropic Dosing and Monitoring.Psychopharmacol Bull. 2024 Jul 8;54(3):8-59. Psychopharmacol Bull. 2024. PMID: 38993656 Free PMC article. Review.
-
T-bet expressing Tr1 cells driven by dietary signals dominate the small intestinal immune landscape.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2025 Jul 4:2025.06.30.662190. doi: 10.1101/2025.06.30.662190. bioRxiv. 2025. PMID: 40747421 Free PMC article. Preprint.
-
Signs and symptoms to determine if a patient presenting in primary care or hospital outpatient settings has COVID-19.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 May 20;5(5):CD013665. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013665.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 35593186 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

