Redox-sensitive δ65Cu isotopic fractionation in the tissue of the scleractinian coral Stylophora pistillata: a biomarker of holobiont photophysiology following volcanic ash exposure
- PMID: 40268344
- PMCID: PMC12050973
- DOI: 10.1093/mtomcs/mfaf011
Redox-sensitive δ65Cu isotopic fractionation in the tissue of the scleractinian coral Stylophora pistillata: a biomarker of holobiont photophysiology following volcanic ash exposure
Abstract
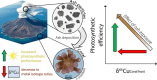
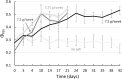
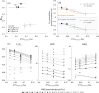
Volcanic ash is a significant source of micronutrients including iron (Fe), copper (Cu), and zinc (Zn) in oligotrophic tropical waters. These bioactive metals enhance primary productivity, influencing local and global biogeochemical cycles. This study explores how volcanic ash exposure affects trace metal uptake and photophysiological response, and how redox-sensitive metal stable isotope measurements in the tissues of the scleractinian coral Stylophora pistillata can provide crucial information on coral health. Controlled coral culture experiments were conducted in which coral nubbins were exposed to varying intensity and duration of volcanic ash. Throughout the experiment, coral symbionts showed enhanced photosynthetic performance irrespective of intensity or duration of ash exposure. Stable isotopes, such as δ65Cu and δ56Fe, in the coral tissue are marked by systematic variations, not associated with intensity or duration of ash exposure. Instead, we suggest biologically modulated redox-sensitive fractionation associated with ash exposure, linked to the coral host's oxidative stress state. This is evidenced by significant correlations between δ65Cu in coral hosts and photophysiology, with lighter Cu isotope ratios associated with higher photosynthetic performances. Hence, we propose that δ65Cu, and more generally redox-sensitive isotopic ratios (i.e. δ56Fe), in coral hosts serves as an indicator of the physiological state of symbiotic corals.
© The Author(s) 2025. Published by Oxford University Press.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures



References
-
- Duggen S, Olgun N, Croot P et al. The role of airborne volcanic ash for the surface ocean biogeochemical iron-cycle: a review. Biogeosciences. 2010;7:827–44. 10.5194/bg-7-827-2010 - DOI
-
- Olgun N, Duggen S, Andronico D et al. Possible impacts of volcanic ash emissions of Mount Etna on the primary productivity in the oligotrophic Mediterranean Sea: results from nutrient-release experiments in seawater. Mar Chem. 2013;152:32–42. 10.1016/j.marchem.2013.04.004 - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

