Radiographic findings in patients suspected of subacromial impingement syndrome in relation to shoulder pain and disability
- PMID: 40268775
- PMCID: PMC12361306
- DOI: 10.1007/s00256-025-04916-3
Radiographic findings in patients suspected of subacromial impingement syndrome in relation to shoulder pain and disability
Abstract
Objective: The aim was to study the association between specific radiographic findings and patient reported shoulder pain and disability in patients suspected of subacromial impingement syndrome (SIS).
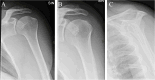
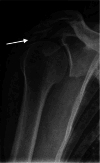
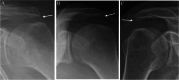
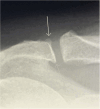
Materials and methods: This cross-sectional study used baseline data from a prospective study. Study population included patients age 18 to 63 years, referred to orthopaedic clinic on suspicion of SIS. Radiographic findings before first visit to a department of orthopaedic surgery comprised subacromial calcifications, acromial morphological characteristics (i.e. acromial type and spur), acromioclavicular osteoarthritis, signs of previous glenohumeral dislocation (Bankart/Hill-Sachs lesions), and architectural measures (i.e. acromial tilt, acromion index, and lateral acromial angle). Shoulder pain and disability were evaluated using the Oxford Shoulder Score (OSS) from patient's response to a questionnaire at first visit to the public department of orthopaedic surgery or before surgery for SIS. A low OSS was defined as having a score < 25. Associations between the radiographic findings and low OSS were analysed using logistic regression.
Results: The population comprised 825 patients. Median time between radiographic examination and completion of the questionnaire was 9 days (SD = 27.1). In adjusted analysis, we found a statistically significant association for lateral spur especially birdbeak type (OR = 2.24 (95% CI 1.36-3.71)), Bankart/Hill-Sachs lesion (OR = 2.49 (95% CI 1.38-4.48)), and acromial tilt > 35° (OR = 0.62 (95% CI 0.41-0.94)). Female sex (OR = 2.25 (95% CI 1.59-3.18)) was also associated with low OSS.
Conclusion: In terms of associations with patient-reported shoulder pain and disability, lateral spurs, with emphasis on birdbeak type, Bankart/Hill-Sachs lesions, and acromial tilt > 35°, seemed clinically important.
Keywords: Impingement; Oxford shoulder score; Radiograph; Shoulder; Subacromial pain.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards. Conflict of interest: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


References
-
- Bosworth BM. Calcium deposits in the shoulder and subacromial bursitis: a survey of 12,122 shoulders. JAMA. 1941;116:2477–82.
-
- Sundhedsstyrelsen (Danish Health and Medicines Authority). National klinisk retningslinje for diagnostik og behandling af patienter med udvalgte skulderlidelser [National clinical guidelines for diagnosis and treatment of patients with selected shoulder disorders]. 2013 Available from: https://www.sst.dk/-/media/Udgivelser/2021/NKR_skulder/NKR-udvalgte-skul....
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

