Nkx2.7 is a conserved regulator of craniofacial development
- PMID: 40268889
- PMCID: PMC12019251
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-025-58821-3
Nkx2.7 is a conserved regulator of craniofacial development
Abstract
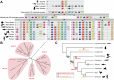
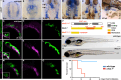
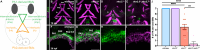
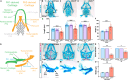
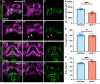
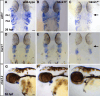
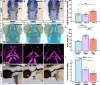
Craniofacial malformations arise from developmental defects in the head, face, and neck with phenotypes such as 22q11.2 deletion syndrome illustrating a developmental link between cardiovascular and craniofacial morphogenesis. NKX2-5 is a key cardiac transcription factor associated with congenital heart disease and mouse models of Nkx2-5 deficiency highlight roles in cardiac development. In zebrafish, nkx2.5 and nkx2.7 are paralogues in the NK4 family expressed in cardiomyocytes and pharyngeal arches. Despite shared cellular origins of cardiac and craniofacial tissues, the function of NK4 factors in head and neck patterning has not been elucidated. Molecular evolutionary analysis of NK4 genes shows that nkx2.5 and nkx2.7 are ohnologs resulting from whole genome duplication events. Nkx2.7 serves as a previously unappreciated regulator of branchiomeric muscle and cartilage formation for which nkx2.5 cannot fully compensate. Mechanistically, our results highlight that Nkx2.7 patterns the cranial neural crest and functions upstream of Endothelin1 to inhibit Notch signals. Together, our studies shed light on an evolutionarily conserved Nkx transcription factor with unique functions in vertebrate craniofacial development, advancing our understanding of congenital head and neck deformities.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Nkx2.5 regulates endothelin converting enzyme-1 during pharyngeal arch patterning.Genesis. 2017 Mar;55(3):10.1002/dvg.23021. doi: 10.1002/dvg.23021. Epub 2017 Feb 10. Genesis. 2017. PMID: 28109039 Free PMC article.
-
mef2ca is required in cranial neural crest to effect Endothelin1 signaling in zebrafish.Dev Biol. 2007 Aug 1;308(1):144-57. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2007.05.018. Epub 2007 May 24. Dev Biol. 2007. PMID: 17574232 Free PMC article.
-
Tgfbeta3 regulation of chondrogenesis and osteogenesis in zebrafish is mediated through formation and survival of a subpopulation of the cranial neural crest.Mech Dev. 2010 Jul-Aug;127(7-8):329-44. doi: 10.1016/j.mod.2010.04.003. Epub 2010 Apr 18. Mech Dev. 2010. PMID: 20406684
-
Understanding endothelin-1 function during craniofacial development in the mouse and zebrafish.Birth Defects Res C Embryo Today. 2004 Jun;72(2):190-9. doi: 10.1002/bdrc.20007. Birth Defects Res C Embryo Today. 2004. PMID: 15269892 Review.
-
Molecular dissection of craniofacial development using zebrafish.Crit Rev Oral Biol Med. 2002;13(4):308-22. doi: 10.1177/154411130201300402. Crit Rev Oral Biol Med. 2002. PMID: 12191958 Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

