Midbrain and pallidal iron changes identify patients with REM sleep behaviour disorder and Parkinson's disease
- PMID: 40268921
- PMCID: PMC12019255
- DOI: 10.1038/s41531-025-00916-1
Midbrain and pallidal iron changes identify patients with REM sleep behaviour disorder and Parkinson's disease
Abstract
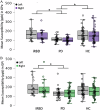
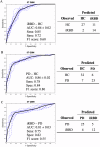
Idiopathic REM sleep behaviour disorder (iRBD) is considered a prodromal form of Parkinson's Disease (PD), potentially exhibiting similar patterns of neurodegeneration, such as brain iron changes. We investigated midbrain and pallidal iron using quantitative susceptibility mapping (QSM) in 16 iRBD patients, 30 PD patients, and 38 age-matched healthy controls (HCs) with 3T MRI. QSM revealed elevated substantia nigra pars compacta (SNc) mean susceptibility in both iRBD and PD patient groups compared to HCs, though iRBD and PD QSM measures did not differ. There were no SN pars reticulata group differences. Mean susceptibility was reduced for PD relative to iRBD and HCs in the globus pallidus externa (GPe). Furthermore, mean susceptibility was reduced for PD relative to iRBD in the GP interna (GPi). GPe/GPi mean susceptibility decreased with PD subgroup motor severity. Consistent with this, QSM in left GPi and MDS-UPDRS-III scores correlated negatively in PD patients, as well as in iRBD and PD patients combined. PD patients also evidenced higher mean susceptibility in the right ventral tegmental area (VTA) compared to iRBD and HCs, consistent with later VTA degeneration. RBD symptomatology did not correlate with QSM values. Combining SNc, GPe, GPi, and VTA QSM values, we distinguished iRBD-HCs, PD-HCs, and iRBD-PD patients at single-subject levels (0.84, 0.86, and 0.81 accuracies), using ROC curve analyses with repeated k-folds cross-validation. Using 3T MRI, QSM values in SNc, GPe, GPi, and VTA demonstrate promise as investigational measures and diagnostic/progression biomarkers of prodromal and early PD.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



References
-
- Barone, P. et al. The PRIAMO study: a multicenter assessment of nonmotor symptoms and their impact on quality of life in Parkinson’s disease. Mov. Disord.24, 1641–1649 (2009). - PubMed
-
- Emre, M., Ford, P. J., Bilgiç, B. & Uç, E. Y. Cognitive impairment and dementia in Parkinson’s disease: practical issues and management. Mov. Disord.29, 663–672 (2014). - PubMed
-
- Prasad, S. et al. Three-dimensional neuromelanin-sensitive magnetic resonance imaging of the substantia nigra in Parkinson’s disease. Eur. J. Neurol.25, 680–686 (2018). - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

