Dual aVß8 Integrin and PD-1 Blockade Overcomes TGFβ-Mediated B-Cell Suppression to Enhance Anti-Tumor Immunity
- PMID: 40269603
- PMCID: PMC12526128
- DOI: 10.1093/neuonc/noaf106
Dual aVß8 Integrin and PD-1 Blockade Overcomes TGFβ-Mediated B-Cell Suppression to Enhance Anti-Tumor Immunity
Abstract
Background: Immunotherapy has revolutionized cancer treatment but has yet to be translated into brain tumors. Studies in other solid tumors suggest a central role of B-cell immunity in driving immune checkpoint blockade efficacy. In glioblastoma (GBM), tumor B cells are driven into a regulatory B-cell state that suppresses immune activation and T-cell function.
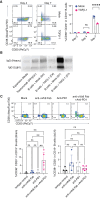
Methods: We used spatially resolved transcriptomics and multiplex immunofluorescence to characterize B-cell neighborhoods within GBM and identify enhanced TGFβ-signaling between myeloid and B cells. We generated conditional knockouts to investigate the effects of TGFβ signaling on B-cell function and survival in vivo. Additionally, we combined TGFβ blockade with PD-1 inhibition to evaluate their combined anti-glioma efficacy.
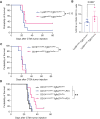
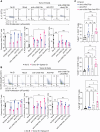
Results: Our findings reveal that myeloid cells are the primary interactors with B cells in GBM through the TGFβ pathway. Pharmacological or genetic TGFβ blockade expanded intratumoral B cells and synergized with PD-1 inhibition to enhance survival (60% tumor eradication in dual-treated mice). Therapeutic efficacy critically depended on B cells, as their depletion abolished survival benefits. Dual αVβ8/PD-1 blockade reduced B-cell-mediated suppression of CD8⁺ T-cell cytotoxicity and increased plasmablast differentiation, while partial efficacy in RagKO mice implicated ancillary roles for innate immunity.
Conclusion: Targeting TGFβ signaling using an anti-αVβ8 blocker can impact anti-tumor immunity through different possible mechanisms, of which we highlight the rescuing of B-cell function through synergy with PD-1 checkpoint blockade therapy. Our work underscores the critical role of intratumoral B-cell immunity in enhancing immunotherapy against brain tumors.
Keywords: B cells; TGFβ; checkpoint-blockade; glioblastoma; tumor microenvironment.
© The Author(s) 2025. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the Society for Neuro-Oncology.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

