High B7-H3 protein expression in Medulloblastoma is associated with metastasis and unfavorable patient outcomes
- PMID: 40269882
- PMCID: PMC12016131
- DOI: 10.1186/s13000-025-01645-y
High B7-H3 protein expression in Medulloblastoma is associated with metastasis and unfavorable patient outcomes
Abstract
Background: Medulloblastoma (MB) is the most common malignant brain tumor in children. Although the 5-year survival rate is approximately 70-80%, the current standard treatment results in severe and long-term side effects. The search for new anticancer immunotherapeutic targets has identified B7-H3 as a promising candidate in various solid tumors. However, the role of B7-H3 in MB remains unclear, and studies reporting its protein expression and association with clinicopathological characteristics are still limited.
Methods: In this study, B7-H3 protein expression was evaluated by immunohistochemistry in seven non-tumor samples and 43 molecularly characterized MB tissues. Its expression profile was correlated with B7-H3 (CD276) mRNA levels, which were previously determined by nCounter, as well as with the patients' clinical features.
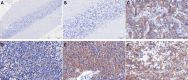
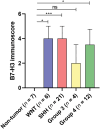
Results: Only 14.3% (1/7) of non-tumor brain and cerebellum tissues showed B7-H3 positivity, whereas 95.6% (41/43) of the MB samples expressed this protein at distinct levels. B7-H3 was found in the cytoplasm and on the membrane of cancer cells. A significant positive correlation was observed between CD276 mRNA and B7-H3 protein levels. Moreover, high expression of B7-H3 protein was associated with worse overall survival and the presence of metastasis at diagnosis.
Conclusions: This is the first study to associate CD276 mRNA and B7-H3 protein levels in MB, revealing a significant positive correlation. We observed that B7-H3 was overexpressed in MB compared to non-tumor brain tissue. High B7-H3 expression was associated with a worse outcome and with the presence of metastasis at diagnosis.
Keywords: B7-H3; CD276; Immunotherapy; Medulloblastoma; Metastasis; Prognostic marker.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: This study was reviewed and approved by the Ethics Committee in Research from Barretos’ Cancer Hospital (Project #1248/2016). Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Northcott PA, Robinson GW, Kratz CP, Mabbott DJ, Pomeroy SL, Clifford SC, et al. Medulloblastoma Nat reviews Disease primers. 2019;5(1):11. - PubMed
-
- Cotter JA, Hawkins C, Medulloblastoma. WHO 2021 and Beyond. Pediatric and developmental pathology: the official journal of the Society for Pediatric Pathology and the Paediatric Pathology Society. 2022;25(1):23–33. - PubMed
-
- Kool M, Korshunov A, Remke M, Jones DT, Schlanstein M, Northcott PA, et al. Molecular subgroups of medulloblastoma: an international meta-analysis of transcriptome, genetic aberrations, and clinical data of WNT, SHH, Group 3, and Group 4 medulloblastomas. Acta Neuropathol. 2012;123(4):473–84. - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

