Asparaginase-associated hyperammonemia
- PMID: 40270200
- PMCID: PMC12358781
- DOI: 10.3324/haematol.2025.287301
Asparaginase-associated hyperammonemia
Abstract
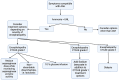
Asparaginase is an essential drug in the treatment of acute lymphoblastic leukemia, and discontinuation of asparaginase therapy due to clinical toxicity or silent inactivation may lead to reduced event-free survival. Common toxicities include hypersensitivity reactions, acute pancreatitis, thrombosis, hepatotoxicity, and hyperlipidemia. In addition, several small case series have described asparaginase-associated hyperammonemia, the true frequency and clinical importance of which, both short- and long-term, remain unclear. Descriptions vary from asymptomatic patients to those with severe, acute encephalopathy leading to withdrawal of asparaginase therapy. The cause and management of the problem remain elusive. This review summarizes current knowledge on asparaginase-associated hyperammonemia, including its pathogenesis, clinical presentation, and possible interventions.
Figures
References
-
- Raja RA, Schmiegelow K, Frandsen TL. Asparaginase-associated pancreatitis in children. Br J Haematol. 2012;159(1):18-27. - PubMed
-
- Henriksen LT, Harila-Saari A, Ruud E, et al. PEG-asparaginase allergy in children with acute lymphoblastic leukemia in the NOPHO ALL2008 protocol. Pediatr Blood Cancer. 2015;62(3):427-433. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources