A simplified frailty score predicts outcome in curatively treated older patients with classical Hodgkin lymphoma
- PMID: 40270216
- PMCID: PMC12485341
- DOI: 10.3324/haematol.2025.287509
A simplified frailty score predicts outcome in curatively treated older patients with classical Hodgkin lymphoma
Abstract
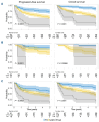
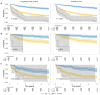
Older patients with classical Hodgkin lymphoma (cHL) have lower tolerance and inferior outcomes after standard chemotherapy regimens. To identify patient-derived indicators of frailty associated with outcome, we retrospectively analyzed patient and disease characteristics, treatment and outcome in a Norwegian population-based cohort of older (≥60 years) patients with cHL diagnosed 2000-2015. We included 279 patients (median age 69 years, range 60-90) treated with curative intent, defined as any typical cHL regimen with ≥50% standard doxorubicin dose in the first cycle. In this Norwegian cohort, treatment-related mortality was 8%, median progression-free survival (PFS) and overall survival (OS) were 7.1 years (95% confidence interval [CI]: 5.0-9.3) and 8.7 years (95% CI: 7.0-10.4), respectively. Multivariable analyses identified patient-derived prognostic factors working independently of stage, histology, and International Prognostic Score. We derived a frailty index ranging from 0-3 with one point each for age ≥70 years, Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group status ≥2, and a Cumulative Illness Rating Scale in Geriatrics score ≥8. Patients were categorized as fit (score 0, 34% of patients), unfit (score 1-2, 60%), and frail (score 3, 7%), with 5-year PFS of 74%, 49%, and 11%, and 5-year OS of 86%, 52%, and 22%, respectively. The proposed frailty score was validated in an external cohort of 792 similarly selected patients from the Swedish Lymphoma Register, where comorbidities were scored based on the Charlson comorbidity index (0-2 vs. 3 or higher). In this comprehensive study, we develop a frailty score for elderly cHL patients to inform clinical decisions and prospective trials evaluating selective therapies for older patients.
Figures

References
-
- Sjöberg J, Halthur C, Kristinsson SY, et al. Progress in Hodgkin lymphoma: a population-based study on patients diagnosed in Sweden from 1973-2009. Blood. 2012;119(4):990-996. - PubMed
-
- Stark GL, Wood KM, Jack F, et al. Hodgkin’s disease in the elderly: a population-based study Br J Haematol. 2002;119(2):432-440. - PubMed
-
- Engert A, Ballova V, Haverkamp H, et al. Hodgkin’s lymphoma in elderly patients: a comprehensive retrospective analysis from the German Hodgkin’s Study Group. J Clin Oncol. 2005;23(22):5052-5060. - PubMed
-
- Björkholm M, Weibull CE, Eloranta S, Smedby KE, Glimelius I, Dickman PW. Greater attention should be paid to developing therapies for elderly patients with Hodgkin lymphoma-a population-based study from Sweden. Eur J Haematol. 2018;101(1):106-114. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

