Anaplastic thyroid cancer: Genetic roles, targeted therapy, and immunotherapy
- PMID: 40271195
- PMCID: PMC12018003
- DOI: 10.1016/j.gendis.2024.101403
Anaplastic thyroid cancer: Genetic roles, targeted therapy, and immunotherapy
Abstract
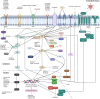
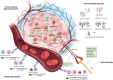
Anaplastic thyroid cancer (ATC) stands as the most formidable form of thyroid malignancy, presenting a persistent challenge in clinical management. Recent years have witnessed a gradual unveiling of the intricate genetic underpinnings governing ATC through next-generation sequencing. The emergence of this genetic landscape has paved the way for the exploration of targeted therapies and immunotherapies in clinical trials. Despite these strides, the precise mechanisms governing ATC pathogenesis and the identification of efficacious treatments demand further investigation. Our comprehensive review stems from an extensive literature search focusing on the genetic implications, notably the pivotal MAPK and PI3K-AKT-mTOR signaling pathways, along with targeted therapies and immunotherapies in ATC. Moreover, we screen and summarize the advances and challenges in the current diagnostic approaches for ATC, including the invasive tissue sampling represented by fine needle aspiration and core needle biopsy, immunohistochemistry, and 18F-fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography/computed tomography. We also investigate enormous studies on the prognosis of ATC and outline independent prognostic factors for future clinical assessment and therapy for ATC. By synthesizing this literature, we aim to encapsulate the evolving landscape of ATC oncology, potentially shedding light on novel pathogenic mechanisms and avenues for therapeutic exploration.
Keywords: ATC; Anaplastic thyroid cancer; Genetic roles; Immunotherapy; Targeted therapy.
© 2024 The Authors. Publishing services by Elsevier B.V. on behalf of KeAi Communications Co., Ltdé.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no competing interests to declare.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Immunotherapy or targeted therapy: What will be the future treatment for anaplastic thyroid carcinoma?Front Oncol. 2023 Mar 17;13:1103147. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2023.1103147. eCollection 2023. Front Oncol. 2023. PMID: 37007127 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Personalized therapy in patients with anaplastic thyroid cancer: targeting genetic and epigenetic alterations.J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2015 Jan;100(1):35-42. doi: 10.1210/jc.2014-2803. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2015. PMID: 25347569 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Molecular therapeutics for anaplastic thyroid cancer.Semin Cancer Biol. 2020 Apr;61:23-29. doi: 10.1016/j.semcancer.2020.01.005. Epub 2020 Jan 25. Semin Cancer Biol. 2020. PMID: 31991166 Free PMC article.
-
Noninvasive anaplastic thyroid carcinoma: report of a case and literature review.Thyroid. 2014 Aug;24(8):1319-24. doi: 10.1089/thy.2013.0586. Epub 2014 Jul 2. Thyroid. 2014. PMID: 24865498 Review.
-
Recent Trends and Potential of Radiotherapy in the Treatment of Anaplastic Thyroid Cancer.Biomedicines. 2024 Jun 10;12(6):1286. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines12061286. Biomedicines. 2024. PMID: 38927493 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Mutational Landmarks in Anaplastic Thyroid Cancer: A Perspective of a New Treatment Strategy.J Clin Med. 2025 Apr 23;14(9):2898. doi: 10.3390/jcm14092898. J Clin Med. 2025. PMID: 40363930 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Kim J., Gosnell J.E., Roman S.A. Geographic influences in the global rise of thyroid cancer. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2020;16(1):17–29. - PubMed
-
- Sung H., Ferlay J., Siegel R.L., et al. Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA A Cancer J Clin. 2021;71(3):209–249. - PubMed
-
- Pizzato M., Li M., Vignat J., et al. The epidemiological landscape of thyroid cancer worldwide: GLOBOCAN estimates for incidence and mortality rates in 2020. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2022;10(4):264–272. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

