Healthy and active aging exercise program for functional health and wellbeing among rural adults: Implementation and evaluation at primary care in Telangana
- PMID: 40271279
- PMCID: PMC12017417
- DOI: 10.4103/jehp.jehp_1467_24
Healthy and active aging exercise program for functional health and wellbeing among rural adults: Implementation and evaluation at primary care in Telangana
Abstract
Background: Population aging is a global phenomenon associated with challenges of physical and cognitive declines, reduced social interaction, and increased risk of mental health issues. Preventive measures to address potential health needs of aging population are essential to promote healthy aging. Physical exercise interventions designed with age-sensitive approach to enhance functional ability and quality of life are essential through community participatory approach. The study aimed evaluation of a multi-component age sensitive home-based physical exercise "Healthy and Active Aging Exercise Protocol (HAAEP)" intervention program on physical health, functional ability, and social interaction among middle-aged to old-aged adults.
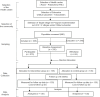
Materials and methods: A randomized control trial was performed applying a 16-week HAAEP program to evaluate functional health (FH) including anthropometric measures and social interaction among 270 community-based adults aged 40-90 years from rural Sangareddy district, Telangana, India.
Results: The Intervention group (IG) and Control group (CG) exhibited differential progress over time, between the group analysis reported significant improvement in TUG (0.0018), 6MWT (0.0292), IPAQ -PA pattern, (0.0194) IPAQ-Sedentary behavior (0.04), BMI (0.0177), Fat percentage (0.0314), Muscle percentage (0.000), Bone and BMR (0.031). Group-based approach in community-friendly settings showed improvement in social interaction, DSSI (0.0120).
Conclusion: Age-sensitive HAAEP program on functional health with social wellbeing, have shown significant positive effect among adults of different age groups, and will be an effective holistic strategy for healthy and active aging.
Keywords: Functional ability; health promotion; healthy aging; physical activity; rural population; social interaction.
Copyright: © 2025 Journal of Education and Health Promotion.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Effect of a home-based exercise program on functional mobility and quality of life in elderly people: protocol of a single-blind, randomized controlled trial.Trials. 2018 Dec 12;19(1):684. doi: 10.1186/s13063-018-3061-1. Trials. 2018. PMID: 30541592 Free PMC article.
-
The effectiveness of web-based programs on the reduction of childhood obesity in school-aged children: A systematic review.JBI Libr Syst Rev. 2012;10(42 Suppl):1-14. doi: 10.11124/jbisrir-2012-248. JBI Libr Syst Rev. 2012. PMID: 27820152
-
A Multilevel Physical Activity Intervention Among Chinese Rural Older Adults (Stay Active While Aging): A Study Protocol for a Clustered Randomized Controlled Trial.Front Public Health. 2022 May 3;10:760457. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2022.760457. eCollection 2022. Front Public Health. 2022. PMID: 35592074 Free PMC article.
-
Exercise-Based Interventions to Enhance Long-Term Sustainability of Physical Activity in Older Adults: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Clinical Trials.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2019 Jul 15;16(14):2527. doi: 10.3390/ijerph16142527. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2019. PMID: 31311165 Free PMC article.
-
Toward the realization of a better aged society: messages from gerontology and geriatrics.Geriatr Gerontol Int. 2012 Jan;12(1):16-22. doi: 10.1111/j.1447-0594.2011.00776.x. Geriatr Gerontol Int. 2012. PMID: 22188494 Review.
References
-
- Daskalopoulou C, Stubbs B, Kralj C, Koukounari A, Prince M, Prina AM. Physical activity and healthy ageing: A systematic review and meta-analysis of longitudinal cohort studies. Ageing Res Rev. 2017;38:6–17. - PubMed
-
- Manchana V. Interrelationships of physical activity, loneliness and social support among older adults: Health and wellbeing in later life. AcadLett. 2021;2:3478.
-
- Manchana V. First. UK: Cambridge Scholars Publishing; Nov 10, 2021. Modern Technological Intervention Advancements for the Physically Challenged and Disabled Population; pp. 151–85. Mediating Cognitive decline and loneliness through physical activity and social connectivity in ageing populations.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous