Natural sulfur compounds in mental health and neurological disorders: insights from observational and intervention studies
- PMID: 40271431
- PMCID: PMC12014460
- DOI: 10.3389/fnut.2025.1534000
Natural sulfur compounds in mental health and neurological disorders: insights from observational and intervention studies
Abstract
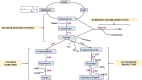
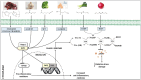
Over the years, the global disease burden of neurological disorders (NDs) and mental disorders (MDs) has significantly increased, making them one of the most critical concerns and challenges to human health. In pursuit of novel therapies against MD and ND, there has been a growing focus on nutrition and health. Dietary sulfur, primarily derived from various natural sources, plays a crucial role in numerous physiological processes, including brain function. This review offers an overview of the chemical composition of several natural sources of the sulfur-rich substances such as isothiocyanates, sulforaphane, glutathione, taurine, sulfated polysaccharides, allyl sulfides, and sulfur-containing amino acids, all of which have neuroprotective properties. A multitude of studies have documented that consuming foods that are high in sulfur enhances brain function by improving cognitive parameters and reduces the severity of neuropathology by exhibiting antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties at the molecular level. In addition, the growing role of natural sulfur compounds in repairing endothelial dysfunction, compromising blood-brain barrier and improving cerebral blood flow, are documented here. Furthermore, this review covers the encouraging results of supplementing sulfur-rich diets in many animal models and clinical investigations, along with their molecular targets in MD, such as schizophrenia, depression, anxiety, bipolar disorder, and autism spectrum disorder, and ND, such as Alzheimer's disease (AD), Parkinson's disease (PD), Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis (ALS), and Multiple Sclerosis (MS). The prospects of natural sulfur compounds show great promise as they have potential applications in nutraceuticals, medicines, and functional foods to enhance brain function and prevent diseases. However, additional research is required to clarify the mechanisms by which it works, enhance its bioavailability, and evaluate its long-term safety for broad use.
Keywords: antioxidant effects; dietary sources and mental disorders; natural sulfur compounds; neuroinflammation; neurological disorders; oxidative stress.
Copyright © 2025 Rana, Katiyar, Arun, Berrios and Kumar.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Dietary glycation compounds - implications for human health.Crit Rev Toxicol. 2024 Sep;54(8):485-617. doi: 10.1080/10408444.2024.2362985. Epub 2024 Aug 16. Crit Rev Toxicol. 2024. PMID: 39150724
-
Polyphenols and Their Impact on the Prevention of Neurodegenerative Diseases and Development.Nutrients. 2023 Aug 4;15(15):3454. doi: 10.3390/nu15153454. Nutrients. 2023. PMID: 37571391 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Naringenin: A prospective therapeutic agent for Alzheimer's and Parkinson's disease.J Food Biochem. 2022 Dec;46(12):e14415. doi: 10.1111/jfbc.14415. Epub 2022 Sep 15. J Food Biochem. 2022. PMID: 36106706 Review.
-
Pre-Clinical Neuroprotective Evidences and Plausible Mechanisms of Sulforaphane in Alzheimer's Disease.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Mar 13;22(6):2929. doi: 10.3390/ijms22062929. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33805772 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Therapeutic Potential of Natural Compounds from Herbs and Nutraceuticals in Alleviating Neurological Disorders: Targeting the Wnt Signaling Pathway.J Agric Food Chem. 2024 Feb 7;72(5):2411-2433. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.3c07536. Epub 2024 Jan 29. J Agric Food Chem. 2024. PMID: 38284360 Review.
References
-
- Oae S. (ed.). Organic Chemistry of Sulfur. Boston, MA: Springer US. (1977).
-
- Huxtable RJ. Biochemistry of Sulfur. Boston, MA: Springer US. (1986).
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

