The burden of colorectal cancer attributable to diet low in whole grains from 1990 to 2021: a global, regional and national analysis
- PMID: 40271437
- PMCID: PMC12014444
- DOI: 10.3389/fnut.2025.1527522
The burden of colorectal cancer attributable to diet low in whole grains from 1990 to 2021: a global, regional and national analysis
Abstract
Background: Colorectal cancer (CRC) is a major global health issue, with rising incidence and mortality rates. Dietary factors, especially whole grains consumption, are critical in determining CRC risk. Understanding CRC deaths and disability-adjusted life years (DALYs) related to low whole grains diets is important for prevention. The purpose of the study is to investigate temporal and geographic trends in CRC deaths and DALYs attributable to diet low in whole grains at the global, regional, and national levels from 1990 to 2021.
Methods: The data on CRC burden attributable to diet low in whole grains from 1990 to 2021 were extracted from the Global Burden of Diseases (GBD) 2021 database. We described the CRC burden attributable to diet low in whole grains across various years, genders, age groups (5-year age groups from 25 to 94 years and 95+ years), different Socio-demographic Index (SDI) regions and countries. To illustrate the temporal trends in the burden of CRC, we calculated the estimated annual percentage change (EAPC) from 1990 to 2021.
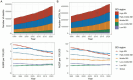
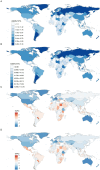
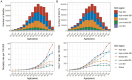
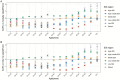
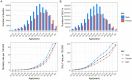
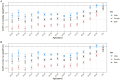
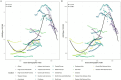
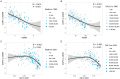
Results: From 1990 to 2021, the global number of CRC deaths attributable to diet low in whole grains increased from 101,813 (95% UI: 42,588 to 151,170) to 186,257 (95% UI: 76,127 to 284,803), representing a 82.94% growth. Similarly, the number of DALYs increased from 2,540,867 (95% UI: 1,050,794 to 3,754,416) to 4,327,219 (95% UI: 1,754,865 to 6,578,232), representing a 70.30% growth. However, both the age-standardized mortality rate (ASMR) and age-standardized DALY rate (ASDR) exhibited a decline, with an EAPC of -0.82 (95% CI: -0.85 to -0.78) and - 0.84 (95% CI: -0.87 to -0.81), respectively. The disease burden is heavier in high SDI and high-middle SDI regions. However, between 1990 and 2021, the only region where both ASMR and ASDR increased was low-middle SDI, while in all other regions, they showed a declining trend. In 2021, East Asia had the highest number of CRC deaths and DALYs attributable to diet low in whole grains at the regional level, followed by Western Europe and High-income North America. Additionally, the burden is greater among males and the elderly. Between 1990 and 2021, the number of CRC deaths attributable to diet low in whole grains rose by 102.13% among males and by 63.20% among females. Generally, both the global age-specific mortality rate and the DALYs rate tend to increase with age. SDI demonstrates a nonlinear "S"-shaped correlation with both ASMR and ASDR of CRC attributable to diet low in whole grains. In 2021, the EAPC in ASMR of CRC attributable to diet low in whole grains was negatively associated with SDI (R = -0.402, p < 0.001), reaching the highest EAPC at approximately SDI of 0.51 and the lowest at 0.85. Similarly, the correlation between EAPC in ASDR and SDI in 2021 exhibited a similar pattern.
Conclusion: Despite a decline in the ASMR and ASDR of CRC attributable to diet low in whole grains from 1990 to 2021 globally, the absolute number of cases continues to increase, with a particularly notable burden observed in High-middle and High SDI regions, as well as among males and the elderly population. It is imperative to intensify efforts in CRC prevention and health education, specifically targeting these high-risk groups to raise public awareness and consumption of whole grains. Furthermore, screening initiatives should be intensified among these demographics to address the elevated risk of CRC mortality due to insufficient whole grains consumption.
Keywords: colorectal cancer; death; diet low in whole grains; disability-adjusted life years; global burden of disease; global burden of disease colorectal cancer.
Copyright © 2025 Ma, Ni, Mei, Chen and Guo.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Global, regional, and national analyses of the burden of colorectal cancer attributable to diet low in milk from 1990 to 2019: longitudinal observational study.Front Nutr. 2024 Jul 22;11:1431962. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2024.1431962. eCollection 2024. Front Nutr. 2024. PMID: 39104758 Free PMC article.
-
Global, regional, and national burden of chronic kidney disease attributable to high sodium intake from 1990 to 2019.Front Nutr. 2023 Mar 2;10:1078371. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2023.1078371. eCollection 2023. Front Nutr. 2023. PMID: 36937353 Free PMC article.
-
The global burden of colorectal cancer attributable to high body-mass index in 204 countries and territories: findings from 1990 to 2021 and predictions to 2035.Front Nutr. 2024 Nov 20;11:1473851. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2024.1473851. eCollection 2024. Front Nutr. 2024. PMID: 39634543 Free PMC article.
-
Evolving landscape of colorectal cancer: Global and regional burden, risk factor dynamics, and future scenarios (the Global Burden of Disease 1990-2050).Ageing Res Rev. 2025 Feb;104:102666. doi: 10.1016/j.arr.2025.102666. Epub 2025 Jan 18. Ageing Res Rev. 2025. PMID: 39828028 Review.
-
The Burden of Cardiovascular Diseases Attributed to Diet High in Sugar-Sweetened Beverages in 204 Countries and Territories From 1990 to 2019.Curr Probl Cardiol. 2024 Jan;49(1 Pt A):102043. doi: 10.1016/j.cpcardiol.2023.102043. Epub 2023 Aug 17. Curr Probl Cardiol. 2024. PMID: 37595857 Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

