Pyruvate and related energetic metabolites modulate resilience against high genetic risk for glaucoma
- PMID: 40272416
- PMCID: PMC12021409
- DOI: 10.7554/eLife.105576
Pyruvate and related energetic metabolites modulate resilience against high genetic risk for glaucoma
Abstract
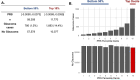
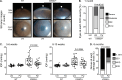
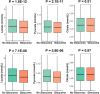
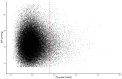
A glaucoma polygenic risk score (PRS) can effectively identify disease risk, but some individuals with high PRS do not develop glaucoma. Factors contributing to this resilience remain unclear. Using 4,658 glaucoma cases and 113,040 controls in a cross-sectional study of the UK Biobank, we investigated whether plasma metabolites enhanced glaucoma prediction and if a metabolomic signature of resilience in high-genetic-risk individuals existed. Logistic regression models incorporating 168 NMR-based metabolites into PRS-based glaucoma assessments were developed, with multiple comparison corrections applied. While metabolites weakly predicted glaucoma (Area Under the Curve = 0.579), they offered marginal prediction improvement in PRS-only-based models (p=0.004). We identified a metabolomic signature associated with resilience in the top glaucoma PRS decile, with elevated glycolysis-related metabolites-lactate (p=8.8E-12), pyruvate (p=1.9E-10), and citrate (p=0.02)-linked to reduced glaucoma prevalence. These metabolites combined significantly modified the PRS-glaucoma relationship (Pinteraction = 0.011). Higher total resilience metabolite levels within the highest PRS quartile corresponded to lower glaucoma prevalence (Odds Ratiohighest vs. lowest total resilience metabolite quartile=0.71, 95% Confidence Interval = 0.64-0.80). As pyruvate is a foundational metabolite linking glycolysis to tricarboxylic acid cycle metabolism and ATP generation, we pursued experimental validation for this putative resilience biomarker in a human-relevant Mus musculus glaucoma model. Dietary pyruvate mitigated elevated intraocular pressure (p=0.002) and optic nerve damage (p<0.0003) in Lmx1bV265D mice. These findings highlight the protective role of pyruvate-related metabolism against glaucoma and suggest potential avenues for therapeutic intervention.
Keywords: cell biology; genetics; genomics; glaucoma; glaucoma resilience; metabolomics; mouse; pyruvate; tricarboxylic acid cycle.
© 2025, Li, Tolman et al.
Conflict of interest statement
KL, AS, KS, OZ, KH, AH, YR, CM, CZ, PH, JK No competing interests declared, NT inventor on patents/patent applications related to the use of ethyl pyruvate to treat glaucoma entitled "Pyruvate and Related Energetic Metabolites Modulate Resilience Against High Genetic Risk for Glaucoma" (U.S. 63/733985) and "Prevention and Treatment of Conditions Using Ethyl Pyruvate" (PCT/US24/20798), NV has acted as a paid consultant or lecturer to Santen, Thea, NovaEye, Glaukos, and Elios, NZ reports consulting fees from Character Biosciences, RD reports being a scientific co-founder, consultant, and equity holder for Pensieve Health (pending) and being a consultant for Variant Bio and Character Bio, AK has acted as a paid consultant or lecturer to Abbvie, Aerie, Allergan, Google Health, Heidelberg Engineering, Novartis, Reichert, Santen, Thea and Topcon, JW reports consulting fees from Editas and CRISPR Therapeutics, SJ founder of Myco Advising LLC, and Qura Inc and advises Starlight Bio Inc with no overlap to the currently presented research. Inventor on patents/patent applications related to the use of ethyl pyruvate to treat glaucoma entitled "Pyruvate and Related Energetic Metabolites Modulate Resilience Against High Genetic Risk for Glaucoma" (U.S. 63/733985) and "Prevention and Treatment of Conditions Using Ethyl Pyruvate" (PCT/US24/20798), LP reports consulting honoraria from Twenty Twenty
Figures






Update of
-
Pyruvate and Related Energetic Metabolites Modulate Resilience Against High Genetic Risk for Glaucoma.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2025 Mar 10:2025.01.18.633745. doi: 10.1101/2025.01.18.633745. bioRxiv. 2025. Update in: Elife. 2025 Apr 24;14:RP105576. doi: 10.7554/eLife.105576. PMID: 39896457 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
References
-
- Burgess LG, Uppal K, Walker DI, Roberson RM, Tran V, Parks MB, Wade EA, May AT, Umfress AC, Jarrell KL, Stanley BOC, Kuchtey J, Kuchtey RW, Jones DP, Brantley MA. Metabolome-wide association study of primary open angle glaucoma. Investigative Ophthalmology & Visual Science. 2015;56:5020–5028. doi: 10.1167/iovs.15-16702. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bycroft C, Freeman C, Petkova D, Band G, Elliott LT, Sharp K, Motyer A, Vukcevic D, Delaneau O, O’Connell J, Cortes A, Welsh S, Young A, Effingham M, McVean G, Leslie S, Allen N, Donnelly P, Marchini J. The UK Biobank resource with deep phenotyping and genomic data. Nature. 2018;562:203–209. doi: 10.1038/s41586-018-0579-z. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- New York Fund for Innovation in Research and Scientific Talent EMPIRE CU19-2660/Empire State Development
- EY018606/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- EY036460/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- EY032507/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 EY018606/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 EY019007/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- Vision Core P30EY019007/Columbia University
- R01 EY036460/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 015473/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 032559/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 EY031424/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- K23 EY032634/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- EY014104/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 EY032507/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- R35 GM124836/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- EY032062/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- 1K23EY032634/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P30 EY014104/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- R01EY031424/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 EY032062/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- R35-GM124836/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

