Habitat radiomics assists radiologists in accurately diagnosing lymph node metastasis of adenocarcinoma of the esophagogastric junction
- PMID: 40272618
- PMCID: PMC12021776
- DOI: 10.1186/s13244-025-01969-9
Habitat radiomics assists radiologists in accurately diagnosing lymph node metastasis of adenocarcinoma of the esophagogastric junction
Abstract
Objectives: This study aimed to develop a habitat radiomics (HR) model capable of preoperatively predicting lymph node metastasis (LNM) in adenocarcinoma of the esophagogastric junction (AEG) and to implement its use in clinical practice.
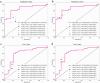
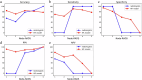
Methods: In this retrospective analysis, 337 patients from three centers were enrolled and divided into three cohorts: training, validation, and test (208, 52, and 77 patients, respectively). We constructed HR models, conventional radiomics models, and combined models to identify LNM in AEG. The area under the curve (AUC) was employed to identify the optimal model, which was then evaluated for assisting radiologists in the empirical and RADS groups in diagnosing LNM. Finally, the prediction process of the optimal model was visualized using SHAP plots.
Results: The HR model demonstrated superior performance, achieving the highest AUC values of 0.876, 0.869, and 0.795 in the training, validation, and test cohorts, respectively. Regardless of seniority, the empirical group of radiologists showed a significant improvement in the AUC and accuracy when using the HR model, compared to working alone (p < 0.05). Furthermore, the RADS group radiologists exhibited strong reclassification ability, effectively reevaluating patients with false-negative LN initially classified as Node-RADS score 1 or 2 by themselves.
Conclusion: The HR model facilitates the accurate prediction of LNM in AEG and holds potential as a valuable tool to augment radiologists' diagnostic capabilities in daily clinical practice.
Critical relevance statement: The habitat radiomics model could accurately predict the lymph node status of adenocarcinoma in the esophagogastric junction and assist radiologists in improving diagnostic efficacy, which lays the foundation for accurate staging and effective treatment.
Key points: Accurate lymph node diagnosis in esophagogastric junction adenocarcinoma is beneficial for prognosis. Habitat radiomics model accurately predicted and assisted physicians in diagnosing lymph nodes. The habitat model effectively reclassified false-negative lymph nodes at Node-RADS 1 and 2.
Keywords: Adenocarcinoma of the esophagogastric junction; Computed tomography; Habitat radiomics; Lymph node; Node-RADS.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: This retrospective study received approval from the institutional review boards (IRB number: 2022002). Consent for publication: Written informed consent was waived due to its retrospective nature. Competing interests: The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures




References
-
- Ford AC, Yuan Y, Moayyedi P (2020) Helicobacter pylori eradication therapy to prevent gastric cancer: systematic review and meta-analysis. Gut 69:2113–2121 - PubMed
-
- Manabe N, Matsueda K, Haruma K (2022) Epidemiological review of gastroesophageal junction adenocarcinoma in Asian countries. Digestion 103:29–36 - PubMed
-
- Zhu Z, Wang Y, Li F et al (2019) Comparison of clinicopathological features and prognosis between adenocarcinoma of esophagogastric junction and adenocarcinoma of gastric antrum. Zhonghua Wei Chang Wai Ke Za Zhi 22:149–155 - PubMed
-
- Urakawa N, Kanaji S, Suzuki S et al (2022) Prognostic and clinicopathological significance of lymph node metastasis in the esophagogastric junction adenocarcinoma. Anticancer Res 42:1051–1057 - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

