Cost-effectiveness of wastewater-based environmental surveillance for SARS-CoV-2 in Blantyre, Malawi and Kathmandu, Nepal: A model-based study
- PMID: 40273116
- PMCID: PMC12021199
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pgph.0004439
Cost-effectiveness of wastewater-based environmental surveillance for SARS-CoV-2 in Blantyre, Malawi and Kathmandu, Nepal: A model-based study
Abstract
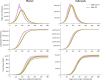
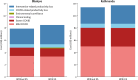
Wastewater-based environmental surveillance (ES) has been demonstrated to provide an early warning signal to predict variant-driven waves of pathogens such as severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2). Our study evaluated the potential cost-effectiveness of ES for SARS-CoV-2 compared with clinical testing alone. We used the Covasim agent-based model of COVID-19 to simulate disease transmission for hypothetical populations in Blantyre, Malawi, and Kathmandu, Nepal. We simulated the introduction of a new immune-escaping variant over 6 months and estimated health outcomes (cases, deaths, and disability-adjusted life years [DALYs]) and economic impact when using ES to trigger a moderate proactive behavioral intervention (e.g., increased use of masks, social distancing) by policymakers versus no ES and hence a delayed reactive intervention. Costs considered included for ES, clinical testing, treatment, and productivity loss for the entire population due to implementation of the behavioral intervention. We calculated the incremental cost-effectiveness ratios and compared these with local willingness-to-pay thresholds: $61 for Malawi and $249 for Nepal. We performed sensitivity analyses to evaluate the impact of key assumptions on the results. Costs are reported in 2022 US dollars. We estimate that if ES were implemented, approximately 600 DALYs would be averted in Blantyre and approximately 300 DALYs averted in Kathmandu, over the six-month period. Considering health system costs, ES was cost-effective in Blantyre and cost-saving in Kathmandu. Cost-effectiveness of ES was highest in settings with low clinical surveillance, high disease severity, and high intervention effectiveness. However, from the societal perspective, ES may not be cost-effective depending on the magnitude of population-wide productivity losses associated with the proactive behavioral intervention and the cost-effectiveness threshold. SARS-CoV-2 ES has the potential to be a cost-saving or cost-effective tool from the health system perspective when linked to an effective public health response. From the societal perspective, however, the length of the behavioral intervention and its consequences for productivity losses of the entire population may make ES not cost-effective. Implementing ES for multiple pathogens may improve its cost-effectiveness.
Copyright: © 2025 Mvundura et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Cost of wastewater-based environmental surveillance for SARS-CoV-2: Evidence from pilot sites in Blantyre, Malawi and Kathmandu, Nepal.PLOS Glob Public Health. 2022 Dec 27;2(12):e0001377. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgph.0001377. eCollection 2022. PLOS Glob Public Health. 2022. PMID: 36962924 Free PMC article.
-
The Economic Impact of Smoking and of Reducing Smoking Prevalence: Review of Evidence.Tob Use Insights. 2015 Jul 14;8:1-35. doi: 10.4137/TUI.S15628. eCollection 2015. Tob Use Insights. 2015. PMID: 26242225 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of four different strategies for SARS-CoV-2 surveillance in the general population (CoV-Surv Study): a structured summary of a study protocol for a cluster-randomised, two-factorial controlled trial.Trials. 2021 Jan 8;22(1):39. doi: 10.1186/s13063-020-04982-z. Trials. 2021. PMID: 33419461 Free PMC article.
-
Modelling of hypothetical SARS-CoV-2 point of care tests for routine testing in residential care homes: rapid cost-effectiveness analysis.Health Technol Assess. 2021 Jun;25(39):1-74. doi: 10.3310/hta25390. Health Technol Assess. 2021. PMID: 34142943 Free PMC article.
-
Multi-gene Pharmacogenomic Testing That Includes Decision-Support Tools to Guide Medication Selection for Major Depression: A Health Technology Assessment.Ont Health Technol Assess Ser. 2021 Aug 12;21(13):1-214. eCollection 2021. Ont Health Technol Assess Ser. 2021. PMID: 34484487 Free PMC article.
References
-
- World Health Organization. WHO COVID-19 dashboard. [cited May 22, 2024]. Available from: https://data.who.int/dashboards/covid19/cases
-
- World Health Organization. WHO COVID-19 Dashboard. [cited May 22, 2024]. Available from: https://data.who.int/dashboards/covid19/deaths
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
