Risk Factors for and Prediction of Early Thromboembolic Disease Following Adult Spinal Deformity Surgery: An Analysis of >7,400 Patients with Spinal Deformity
- PMID: 40273208
- PMCID: PMC12118619
- DOI: 10.2106/JBJS.23.01391
Risk Factors for and Prediction of Early Thromboembolic Disease Following Adult Spinal Deformity Surgery: An Analysis of >7,400 Patients with Spinal Deformity
Abstract
Background: The aim of this study was to determine the risk factors associated with deep vein thrombosis (DVT) or pulmonary embolism (PE) within 30 days after multilevel adult spinal deformity (ASD) surgery and to develop risk prediction models.
Methods: A retrospective observational study was conducted using the American College of Surgeons National Surgical Quality Improvement Program database from 2010 to 2019. Current Procedural Terminology (CPT) codes 22843 and 22844 were used to query the database and to identify patients who underwent surgical correction of ASD with ≥7 levels of posterior instrumentation. The primary outcomes were the incidences of, and risk factors for, postoperative DVT and PE. Multiple logistic regression was utilized to identify variables associated with an elevated risk of DVT or PE within 30 days after surgery and to develop prediction models for assessing risk.
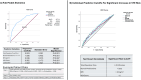
Results: A total of 7,445 patients (56% female; 73% Caucasian; mean age, 61 years) met the inclusion criteria. Postoperatively, the rate of any venous thromboembolism (VTE; i.e., DVT or PE) was 3.4% (254 patients), the rate of DVT was 2.0% (151 patients), and the rate of PE was 1.7% (127 patients). The following independent predictors of any VTE were identified: weight (odds ratio [OR], 1.054; 95% confidence interval [CI]: 1.027 to 1.081), age per decade of life (OR, 1.106; 95% CI: 1.012 to 1.209), body mass index (BMI; OR, 1.032; 95% CI: 1.015 to 1.049), medicated hypertension (OR, 1.523; 95% CI: 1.168 to 1.987), chronic corticosteroid use (OR, 2.654; 95% CI: 1.848 to 3.812), American Society of Anesthesiologists (ASA) class (OR, 1.768; 95% CI: 1.426 to 2.192), and total operative time (OR, 1.002; 95% CI: 1.002 to 1.003) (p < 0.05 for all). When incorporated into a single model, total operative time, BMI, ASA class, and chronic corticosteroid use were associated with VTE risk.
Conclusions: Four major risk factors were identified as being associated with postoperative VTE risk in patients undergoing surgery for ASD. Corticosteroid use for a chronic medical condition was the strongest predictor of VTE risk, followed by ASA class, BMI, and operative time. Knowledge of these risk factors can aid in preoperative risk assessment, informed consent, and medical decision-making, such as in determining the clinical thresholds for VTE testing and chemoprophylaxis.
Level of evidence: Prognostic Level III . See Instructions for Authors for a complete description of levels of evidence.
Copyright © 2025 The Author(s). Published by The Journal of Bone and Joint Surgery, Incorporated.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure: No external funding was received for this work. The Disclosure of Potential Conflicts of Interest forms are provided with the online version of the article ( http://links.lww.com/JBJS/I573 ).
Figures
References
-
- Buesing KL, Mullapudi B, Flowers KA. Deep venous thrombosis and venous thromboembolism prophylaxis. Surg Clin North Am. 2015. Apr;95(2):285-300. - PubMed
-
- Office of the Surgeon General; National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute. The Surgeon General’s call to action to prevent deep vein thrombosis and pulmonary embolism. Rockville: Office of the Surgeon General; 2008. - PubMed
-
- Glassman SD, Hamill CL, Bridwell KH, Schwab FJ, Dimar JR, Lowe TG. The impact of perioperative complications on clinical outcome in adult deformity surgery. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2007. Nov 15;32(24):2764-70. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

