CLN-619, a MICA/B monoclonal antibody that promotes innate immune cell-mediated antitumor activity
- PMID: 40274283
- PMCID: PMC12020772
- DOI: 10.1136/jitc-2024-008987
CLN-619, a MICA/B monoclonal antibody that promotes innate immune cell-mediated antitumor activity
Abstract
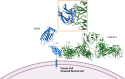
Background: Major histocompatibility complex class I-related protein A and B (MICA/B) are ligands for the natural killer group 2 member D (NKG2D) receptor and are broadly expressed on tumor cells but minimally on normal tissues. When cytotoxic NKG2D-expressing immune cells engage MICA/B, the ligand-expressing cells are targeted for lysis. Cancer cells can evade NKG2D-mediated destruction by shedding MICA/B from their cell surface via proteases present in the tumor microenvironment. CLN-619 is a humanized IgG1 monoclonal antibody (mAb) which binds MICA/B and inhibits shedding resulting in accumulation of MICA/B on the tumor cell surface. CLN-619 may thereby have therapeutic effects in a broad range of malignancies by re-establishing the MICA/B-NKG2D axis to enable NKG2D-mediated, as well as Fc-gamma receptor-mediated, tumor cell lysis.
Methods: CLN-619 was characterized for binding epitope and affinity, effects on surface and soluble levels of MICA/B, and in vitro tumor cell killing. In mouse models, the mAb was tested for tumor growth inhibition. The contribution of the Fc-gamma (Fcγ) 1 domain to CLN-619 activity was also assessed.
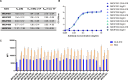
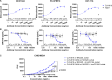
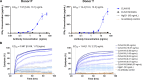
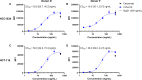
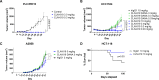
Results: CLN-619 bound with high affinity to the alpha-3 domain of MICA/B without encumbering the interaction with NKG2D on natural killer cells. CLN-619 increased the level of cell surface expression of MICA/B and concomitantly decreased the levels of soluble MICA/B in cell culture assays. Treatment of cancer cell lines with CLN-619 induced antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity and antibody-dependent cellular phagocytosis. CLN-619 resulted in potent inhibition of tumor growth in multiple xenograft models and increased survival of mice in a disseminated cancer model.
Conclusions: CLN-619 inhibited the shedding of MICA/B to effectively restore cytotoxic signaling pathways in immune cells. Potent antitumor activity of CLN-619 as a monotherapy was observed in several preclinical models. Activity of CLN-619 required a functional Fcγ1 domain, suggesting the requirement of simultaneous engagement of NKG2D and cluster of differentiation 16A (CD16A) on immune cells for optimal cytotoxicity. The preclinical data reported here support the assessment of CLN-619 in patients with cancer.
Keywords: Monoclonal antibody; Natural killer - NK.
© Author(s) (or their employer(s)) 2025. Re-use permitted under CC BY-NC. No commercial re-use. See rights and permissions. Published by BMJ Group.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: KAW, CH, NKM, KR, KM, PAB, SY and JSM have ownership in Cullinan Therapeutics, which is seeking to commercialize CLN-619.
Figures

References
-
- Kellner C, Hallack D, Glorius P, et al. Fusion proteins between ligands for NKG2D and CD20-directed single-chain variable fragments sensitize lymphoma cells for natural killer cell-mediated lysis and enhance antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity. Leukemia. 2012;26:830–4. doi: 10.1038/leu.2011.288. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
