Advancements in mechanisms and drug treatments for fibrodysplasia ossificans progressiva
- PMID: 40274382
- PMCID: PMC12021541
- DOI: 10.1631/jzus.B2300779
Advancements in mechanisms and drug treatments for fibrodysplasia ossificans progressiva
Abstract
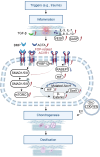
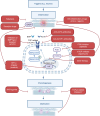
Fibrodysplasia ossificans progressiva (FOP) is a rare genetic disorder characterized by congenital bilateral malformation of the large toe and progressive, extensive, and irreversible heterotopic ossification (HO) of soft tissues throughout the body, leading to severe disabilities. FOP is caused primarily by mutations in activin A receptor type 1 (ACVR1), also known as activin-like kinase 2 (ALK2), which encodes a receptor belonging to the bone morphogenetic protein (BMP) type I family. However, the continuous and complex process of HO in FOP is not yet fully understood, which has impeded the development of therapeutic drugs. Despite surgical removal of HO, which often results in recurrence and expansion of ossification, there is currently no definitive drug treatment available to completely prevent, halt, or reverse the progression of HO in FOP. Currently, researchers are intensively studying the pathogenesis of FOP at various stages and developing promising drug candidates, including saracatinib, palovarotene, and rapamycin. This review provides an overview of progress in understanding the mechanism of FOP and the development of therapeutic drugs, with the goal of providing insights for further research and the development of new treatment methods.
进行性骨化性纤维发育不良(FOP)是一种罕见的遗传性疾病,它以先天性双侧大脚趾畸形和全身软组织进行性、广泛性和不可逆的异位骨化(HO)为特征,最终可导致严重残疾。FOP主要由活化素A受体1(ACVR1,也被称为活化素受体样激酶2,即ALK2)的突变引起,该受体属于骨形态发生蛋白(BMP)I型受体。然而,FOP中复杂的HO形成机制尚未完全明确,这阻碍了治疗药物的开发。手术切除骨化组织常会导致HO的复发和扩大,而目前尚无药物可完全预防、停止或逆转FOP中HO的进展。目前,研究人员正在深入研究各个阶段FOP的发病机制,并开发候选药物,包括saracatinib、palovarotene和rapamycin等。本文就FOP的发病机制及治疗药物的研究进展进行综述,以期为进一步研究和开发新的治疗方法提供参考。.
进行性骨化性纤维发育不良(FOP)是一种罕见的遗传性疾病,它以先天性双侧大脚趾畸形和全身软组织进行性、广泛性和不可逆的异位骨化(HO)为特征,最终可导致严重残疾。FOP主要由活化素A受体1(ACVR1,也被称为活化素受体样激酶2,即ALK2)的突变引起,该受体属于骨形态发生蛋白(BMP)I型受体。然而,FOP中复杂的HO形成机制尚未完全明确,这阻碍了治疗药物的开发。手术切除骨化组织常会导致HO的复发和扩大,而目前尚无药物可完全预防、停止或逆转FOP中HO的进展。目前,研究人员正在深入研究各个阶段FOP的发病机制,并开发候选药物,包括saracatinib、palovarotene和rapamycin等。本文就FOP的发病机制及治疗药物的研究进展进行综述,以期为进一步研究和开发新的治疗方法提供参考。
Keywords: Activin A receptor type 1 (ACVR1); Drug treatment; Fibrodysplasia ossificans progressiva (FOP); Heterotopic ossification (HO); Mechanism.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Palovarotene Inhibits Heterotopic Ossification and Maintains Limb Mobility and Growth in Mice With the Human ACVR1(R206H) Fibrodysplasia Ossificans Progressiva (FOP) Mutation.J Bone Miner Res. 2016 Sep;31(9):1666-75. doi: 10.1002/jbmr.2820. Epub 2016 Mar 12. J Bone Miner Res. 2016. PMID: 26896819 Free PMC article.
-
The obligatory role of Activin A in the formation of heterotopic bone in Fibrodysplasia Ossificans Progressiva.Bone. 2018 Apr;109:210-217. doi: 10.1016/j.bone.2017.06.011. Epub 2017 Jun 16. Bone. 2018. PMID: 28629737 Free PMC article. Review.
-
BMP signaling and skeletal development in fibrodysplasia ossificans progressiva (FOP).Dev Dyn. 2022 Jan;251(1):164-177. doi: 10.1002/dvdy.387. Epub 2021 Jun 26. Dev Dyn. 2022. PMID: 34133058 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Overexpression of Wild-Type ACVR1 in Fibrodysplasia Ossificans Progressiva Mice Rescues Perinatal Lethality and Inhibits Heterotopic Ossification.J Bone Miner Res. 2022 Nov;37(11):2077-2093. doi: 10.1002/jbmr.4617. Epub 2022 Jul 3. J Bone Miner Res. 2022. PMID: 35637634 Free PMC article.
-
Fibrodysplasia ossificans progressiva: middle-age onset of heterotopic ossification from a unique missense mutation (c.974G>C, p.G325A) in ACVR1.J Bone Miner Res. 2012 Mar;27(3):729-37. doi: 10.1002/jbmr.1473. J Bone Miner Res. 2012. PMID: 22131272
References
-
- Blueprint Medicines Corporation , 2019. Safety, tolerability, pharmacokinetics, and food effect of BLU-782 in healthy adults. ClinicalTrials.gov ID NCT 03858075. https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT03858075
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

